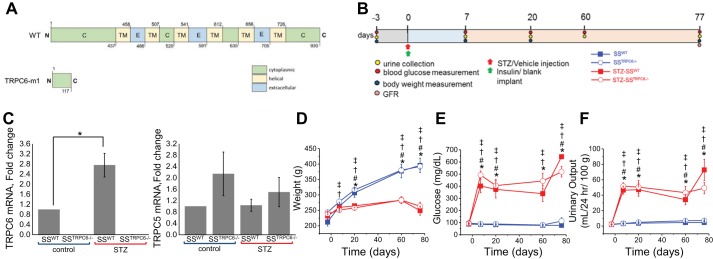
Fig. 1.
Development of STZ-induced DKD in transient receptor potential canonical 6 (Trpc6) knockout and wild-type (WT) rats during the 11-wk protocol. A: scheme of WT TRPC6 and truncated TRPC6-m1 (SSTrpc6−/−), which resulted from a 2-bp insertion leading to a frameshift mutation. B: protocol used for all four experimental groups (vehicle or STZ-treated WT and SSTrpc6−/− rats). C: RT-PCR quantification of Trpc6 and Trpc5 mRNA expression in WT and SSTrpc6−/− rats treated and not treated with STZ (values normalized to 18S); n = 4 rats for SSWT, SSTrpc6−/−, STZ-SSWT, and STZ-SSTrpc6−/−. D–F: development of diabetes in SS and SSTrpc6−/− rats during the 11 wk after STZ injection observed by weight (D), blood glucose (E), and urinary output changes (F). n = 5, 18, 9, and 17 rats for SSWT, SSTrpc6−/−, STZ-SSWT, and STZ-SSTrpc6−/−, respectively. *P < 0.05 for SSWT versus STZ-SSWT, #P < 0.05 for SSWT versus STZ-SSTrpc6−/−, †P < 0.05 for SSTrpc6−/− versus STZ-SSTrpc6−/−, ‡P < 0.05 for SSTrpc6−/− versus STZ-SSWT. DKD, diabetic kidney disease; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; SS, salt-sensitive; STZ, streptozotocin.