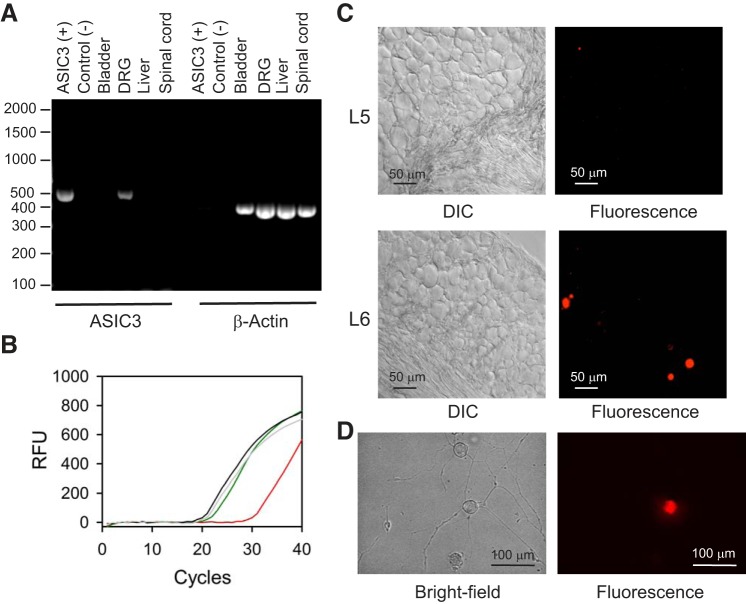
Fig. 1.
Acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) is expressed in sensory neurons. A: reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) demonstrates the presence of transcripts for ASIC3 in dorsal root ganglia (DRG), but not urinary bladder or spinal cord. A construct coding for murine ASIC3 was used as positive control. RNA was isolated with the RNAqueous-4PCR kit and reverse transcription was done with the AccuScript PfuUltra II RT-PCR kit as indicated in materials and methods. The expected size of the PCR products for ASIC3 and β-actin was 437 and 359 bp, respectively. B: representative amplification plots for ASIC3 and β-actin. DNA was extracted from an ear punch collected from wild-type and ASIC3 KO mice as described in materials and methods. Curves indicate amplification from genomic DNA of ASIC3 (wild type, green; ASIC3 KO, red) and β-actin (wild type, gray; ASIC3 KO, black). C: differential interference contrast (DIC) and epifluorescence micrographies captured from cryosections of a paraformaldehyde-fixed DRG [lumbar 5 (L5) and L6] harvested from a mouse injected in the bladder wall with DiI. Note that DiI-labeled cells are present in L6, but not in L5. Representative of 4 independent experiments. D: bright-field and epifluorescence micrographies of isolated sensory neurons harvested from mice injected with DiI in the bladder wall.