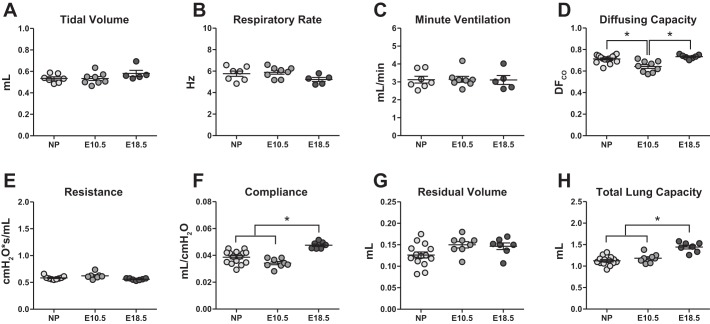
Fig. 1.
Baseline pulmonary function is altered during pregnancy in C57BL/6 mice. Pulmonary function testing was performed on nonpregnant (n = 7–15) and pregnant mice at embryonic day (E)10.5 (n = 7–9) or E18.5 (n = 5–7). Whole body plethysmography was used to measure tidal volume (A), respiratory rate (B), and minute ventilation (C) from unanesthetized animals. Following anesthesia and tracheal cannulation, pulmonary diffusing capacity (D) was measured by gas chromatography, and dynamic resistance (E) and compliance (F) were measured using a Flexivent system with forced oscillation technique. Following euthanasia, the residual volume (G) and total lung capacity (H) were calculated from pressure volume curves. Bars represent means ± SE. All data sets were analyzed using one-way ANOVAs with Bonferroni post hoc correction, where *P < 0.05.