Fig. 3.
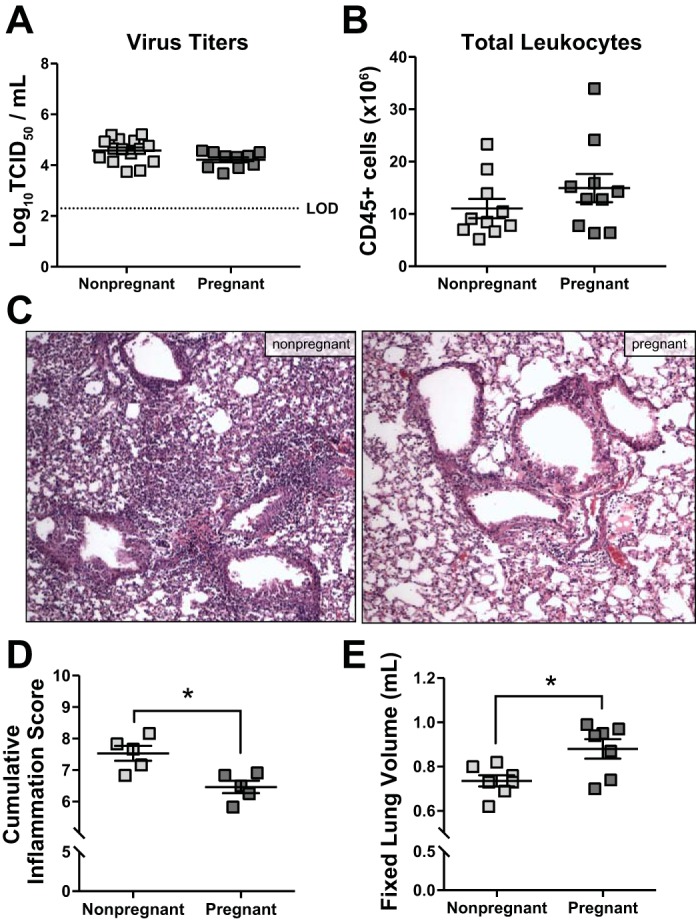
Pulmonary inflammatory responses to influenza A virus (IAV) infection are similar between pregnant and nonpregnant female mice. Nonpregnant (n = 5–15) and pregnant [embryonic day (E)10.5; n = 5–10] mice were inoculated with a sublethal dose of IAV or vehicle (mock). Females were euthanized 8 days postinoculation (dpi), corresponding to E18.5 in pregnant dams. Infectious virus (A), determined by 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50), and total numbers of CD45+ inflammatory cells (B), determined by flow cytometry, were quantified from the lungs. Histopathology was performed on fixed lung tissue, and representative images from H&E-stained sections were taken at ×20 magnification (C). D: cumulative pulmonary inflammation was quantified based on a 0–3 scale for bronchiolitis, perivasculitis, alveolitis, and edema, and the sums of each score are presented. E: fixed lung volume was determined from inflated lungs by water displacement. Bars represent means ± SE. The stippled line in A represents the limit of detection (LOD). All data sets were analyzed using Student’s t-test, where *P < 0.05.
