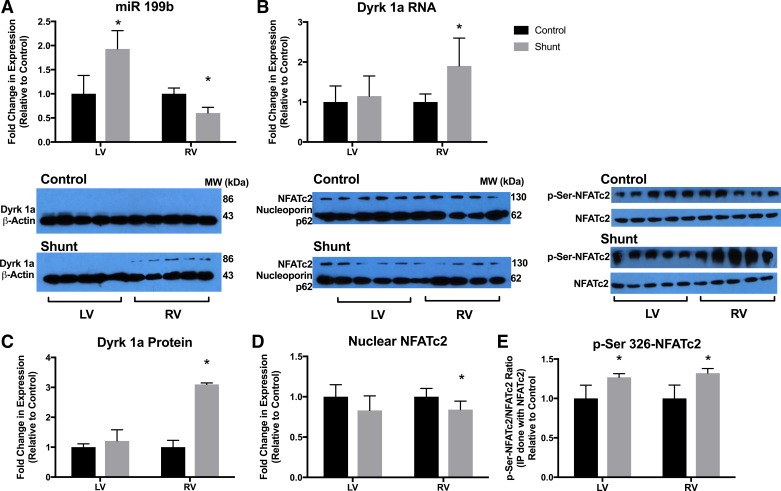
Fig. 1.
The microRNA (miR)-199b dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1a (Dyrk1a)-nuclear factor of activated cell (NFAT) axis. A: miR-199b expression was increased in the shunt left ventricle (LV) and decreased in the shunt right ventricle (RV) compared with the control LV and RV. B: Dyrk1a RNA expression was increased in the shunt RV compared with control RV. MiRNA and mRNA expression was quantified by PCR. Values are means ± SE. C: Dyrk1a protein expression was increased in the shunt RV compared with the control RV. There was no difference in Dyrk1a protein between shunt and control LVs. D: the nuclear fraction of cells was separated from LV and RV homogenates, and NFATc2 was quantified. There was significantly less NFATc2 in the nuclear isolate from the shunt RV compared with control RV. There was no difference in LV nuclear NFATc2. E: the cytosolic fraction of LV and RV homogenates was immunoprecipitated using NFATc2 and then immunoblotted using phosphorylated (Ser326) NFATc2 (p-Ser326-NFATc2) and NFATc2 for quantification. p-Ser326-NFATc2 did not translocate to the nucleus to promote transcription and was more abundant in the LV and RV of shunt lambs compared with control lambs. In C–E, protein expression was quantified by Western blot analysis. For each protein, immunoblots of different membranes were performed in parallel using identical aliquots of the same protein homogenate. Bar graphs and results represent densitometry performed on individual samples (n = 5 in all groups). *P < 0.05 vs. control.