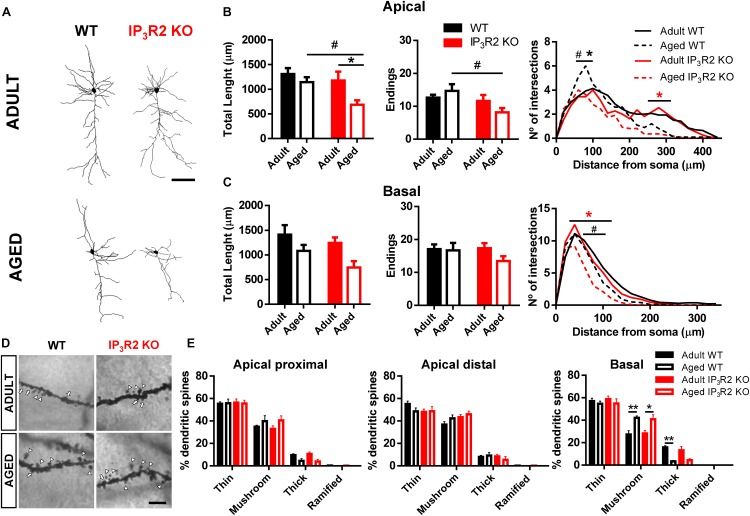
FIGURE 3.
Aging leads to a dendritic refinement of mPFC layer V pyramidal neurons in IP3R2 KO mice. (A) Representative 3D reconstructions of layer V mPFC neurons from WT and IP3R2 KO mice (adults or aged; scale bar = 100 μm). (B,C) Morphological parameters of apical (B) and basal (C) dendrites by assessing total dendritic length, number of endings and Sholl intersections (n = 10–14 neurons per group; two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). (D) Representative images of basal dendritic segments of each experimental group; scale bar = 5 μm; arrowheads, mushroom-type; arrow, thick-type. (E) Percentage of each spine type at proximal and distal segments of apical dendrites, and basal dendrites (n = 6–14 neurons per group; two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). WT (adults and aged) mice are represented either by filled/unfilled black bars or black line/dashed line, while IP3R2 KO (adults and aged) are represented either by filled/unfilled red bars or red line/dashed line. Data plotted as mean ± SEM. ∗Denotes the effect of age; #denotes the effect of genotype. Sholl analysis: black ∗, refers to difference between WT; red ∗, refers to difference between IP3R2 KO; #, ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01.