Figure 1.
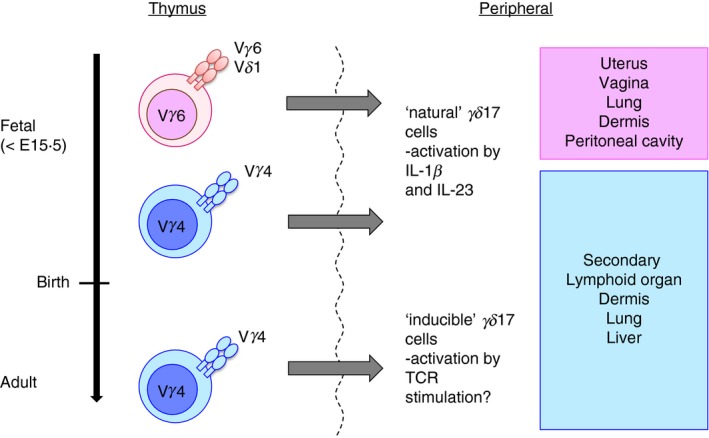
Distinct features of γδ17 cell subset and suggested model of ‘natural’ γδ17 cells versus ‘inducible’ γδ17 cells. Vγ6+ γδ T cells express the invariant Vγ6/Vδ1 T‐cell receptor (TCR), develop only in the late embryonic thymus, and preferentially localize to the uterus, vagina, lung, dermis and peritoneal cavity. On the other hand, Vγ4+ γδ T cells develop in both fetal and adult thymus and have a more diverse TCR repertoire. These cells circulate in blood and reside in the dermis, lung, liver and secondary lymphoid organs. In according to Haas et al.50 ‘natural’ γδ17 cells (Vγ6+ and part of Vγ4+) developed before birth acquire interleukin‐17 (IL‐17) ‐producing ability in thymus and produce IL‐17 stimulated by IL‐1β and IL‐23 in the periphery. Conversely, IL‐17 production induced by TCR signalling was also reported.56 Naive γδ T cells developed after birth may egress the thymus as ‘inducible’ γδ17 cells (mostly Vγ4+) and differentiate to produce IL‐17 after encounter with antigen.
