Figure 3.
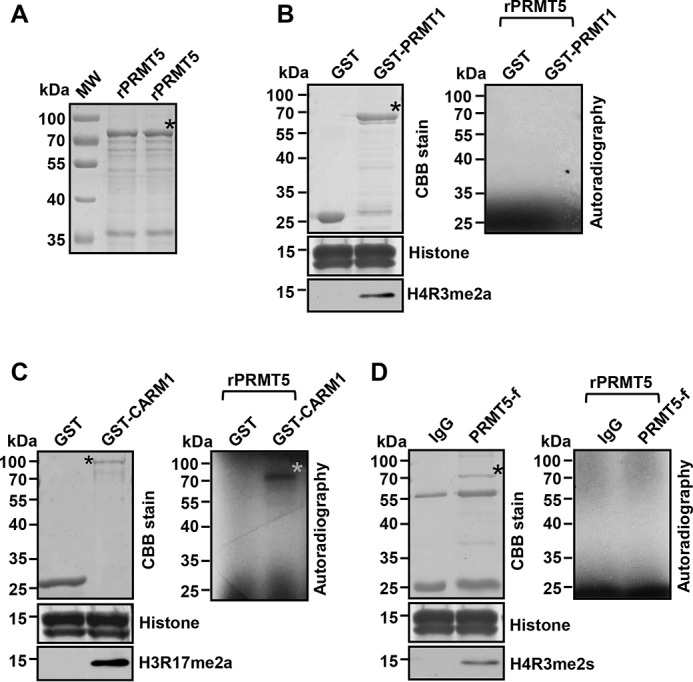
CARM1 methylates PRMT5. A, SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant PRMT5 (rPRMT5) from E. coli as the substrate for following in vitro methylation assays. B, SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant GST-PRMT1 and GST control from E. coli (top left). SDS-PAGE analysis of free histones stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) (middle left). Western blot analysis of free histones from an in vitro methylation assay with H4R3me2a antibody (bottom left). Autoradiographic image from an in vitro methylation assay with GST-PRMT1 or GST control (right). C, SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant GST-CARM1 and GST control from E. coli (top left). SDS-PAGE analysis of free histones stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) (middle left). Western blot analysis of free histones from an in vitro methylation assay with H3R17me2a antibody (bottom left). Autoradiographic image from an in vitro methylation assay with GST-CARM1 or GST control (right). A gray asterisk denotes the positive 3H-labeled PRMT5 band. D, SDS-PAGE analysis of IgG control (top left) and of FLAG-PRMT5 immunoprecipitated from Lys-562 cells overexpressing FLAG-tagged PRMT5. SDS-PAGE analysis of free histones stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) (middle left). Western blot analysis of free histones from an in vitro methylation assay with H4R3me2s antibody (bottom left). Autoradiographic image from an in vitro methylation assay with FLAG-PRMT5 or IgG control (right). Black asterisks denote the fusion proteins in assays.
