Figure 1.
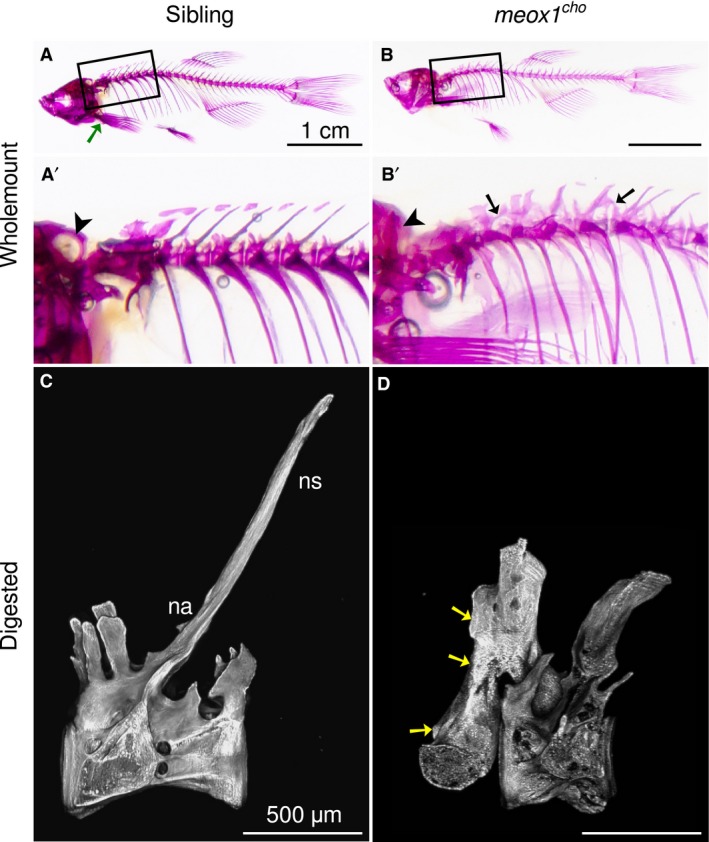
Bone defects coalesce anteriorly in meox1 cho mutant zebrafish. (A,B) Lateral views of whole‐mount alizarin red‐stained 32‐mm standard length adult siblings and homozygotes reveal that bone defects within meox1 cho homozygotes are confined to the axial skeleton. The boxed regions are magnified in (A′) and (B′). A green arrow indicates the location of the pectoral girdle. (A′,B′) The exoccipital foramen is readily discerned in siblings (A′, arrowhead, n = 6/6) and is not evident in whole‐mount meox1 cho homozygous mutants (B′, arrowhead, n = 6/6). Vertebral fusion is evident in vertebræ across neural arches (B′, arrows, n = 6/6). (C) Lateral maximum intensity Z‐projection of a chemically isolated vertebra shows the morphology typical of a vertebra from the anterior region of the wild‐type zebrafish spine. (D) Lateral view of a chemically isolated vertebra involved in an apparent anterior fusion in a meox1 cho adult mutant. Fusion occurred between neural arches (arrows); however, only one vertebral centrum was incorporated. na, neural arch; ns, neural spine. Scale bars: 1 cm (A,B); 500 μm (C,D).
