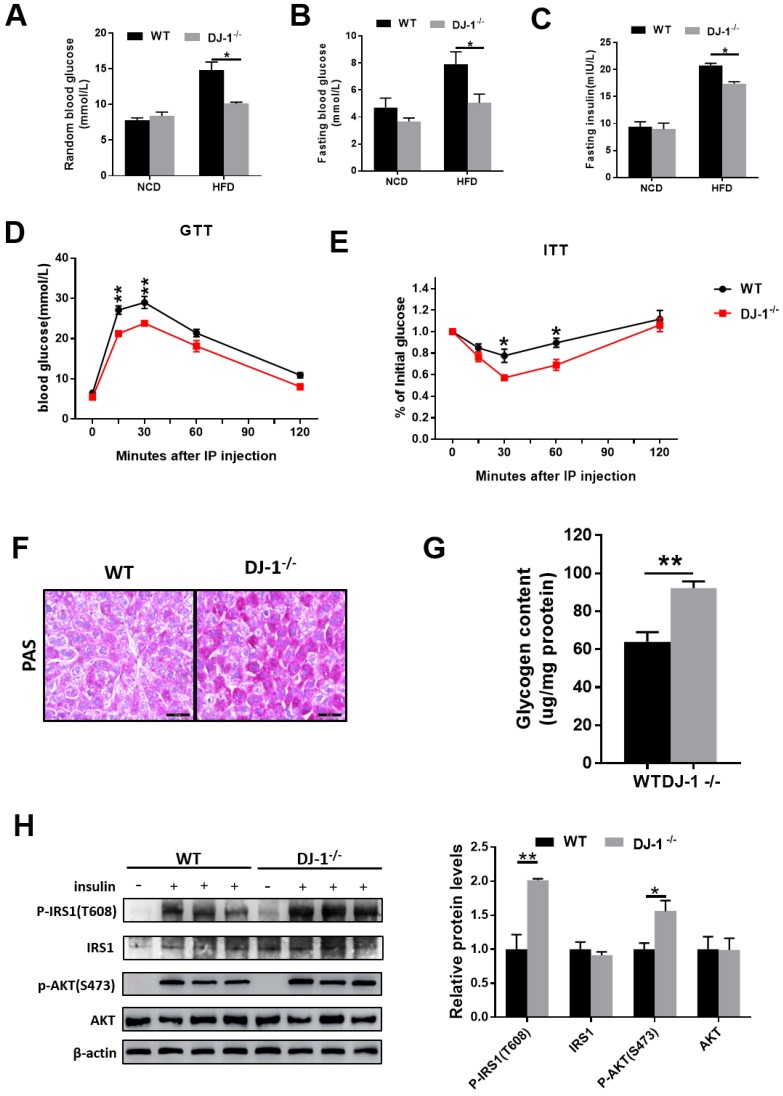
Figure 2.
Deletion of DJ-1 improved HFD-induced insulin resistance and glucose metabolic disorder. (A)Random blood glucose and (B) fasting blood glucose (fasted for 6 h) of WT and DJ-1-/- mice that were fed an NCD or HFD for 24 weeks. (C) Fasting blood serum insulin levels of DJ-1-/- and WT mice that after fed an HFD for 24 weeks. (D, E) The level of blood glucose in a glucose tolerance test (GTT) and an insulin tolerance test (ITT) in WT and DJ-1-/- mice after 24 weeks HFD treatment. (F) Glycogen accumulation in liver sections by PAS staining in WT and DJ-1-/- mice that fed HFD for 24 weeks. (G) Liver glycogen contents in WT and Dj-1-/- mice after HFD administration for 24 weeks. (H) Representative western blot for phosphorylation and total IRS1 and AKT, in the liver tissues from DJ-1-/- and WT mice after HFD administration for 24 weeks. β-actin served as the loading control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.