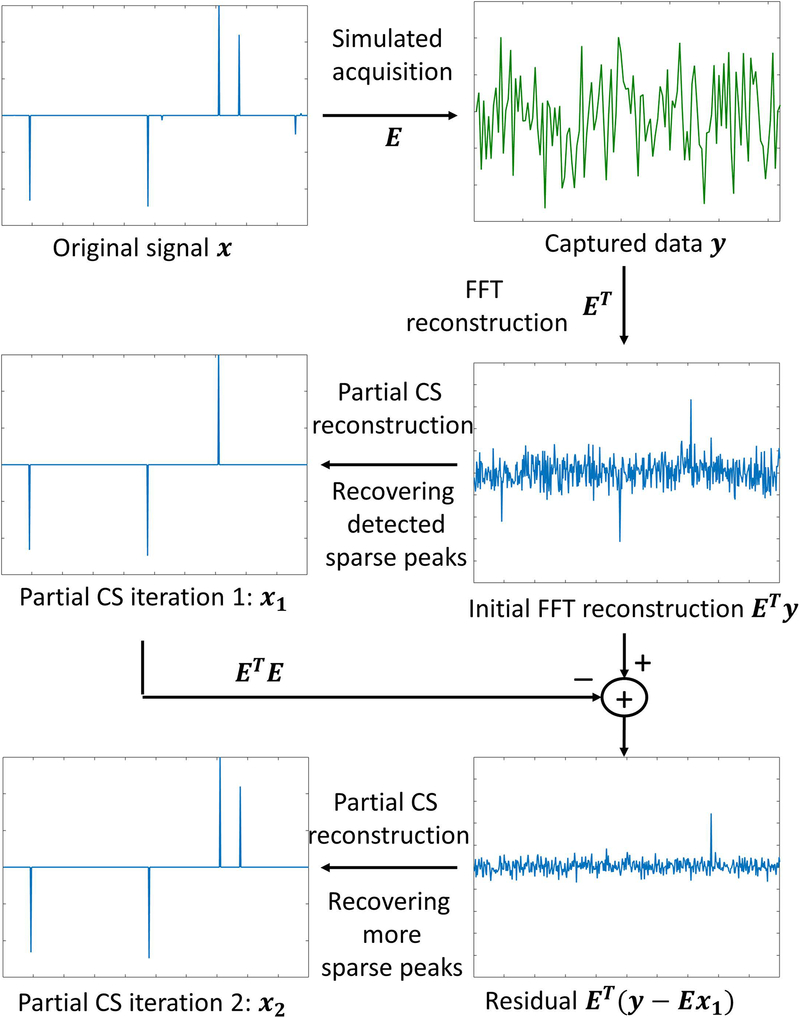
Figure 2:
General concept used in CS. The original signal x should be sparse, and the system matrix E should be incoherent. The effect of this is that ETy, where y is the k-space data and ET is the adjoint of E, should be basically sparse peaks mixed with noise-like artifacts, which are easily recovered by a nonlinear CS reconstruction. Most significant peaks are usually recovered at the initial iteration . However, remaining sparse elements can be seen when the residual is mapped back to image domain, via , and they are recovered in the following iterations, such as .