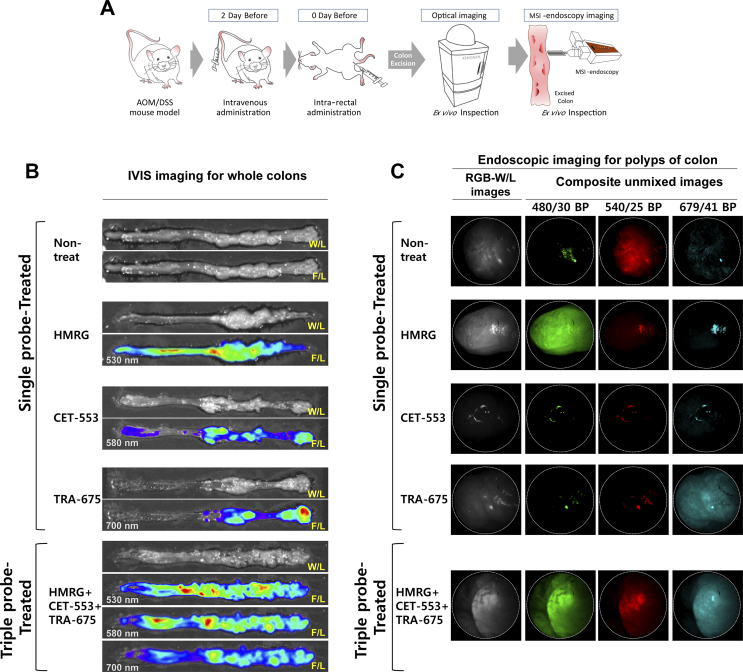
Figure 2.
Ex vivo colon tissue imaging with multispectral endoscope and IVIS system.
(A) An illustrated flow showing the performed ex vivo experiments. Mouse is administered with fluorescence probes and examined by optical instrument and MSI-endoscopy. Individually targeted ex vivo colon polyp images from mouse treating with single probe only and triple probes simultaneously. Excised colons were scanned for IVIS wide-field fluorescence imaging (B) and imaged with multi-spectral fluorescence endoscope system (C). The whole view of white-light (W/L) and IVIS optical fluorescence-light (F/L) imaging of colon is shown (B). Apply of two antibodies (i.v.) and HMRG (spraying) sequentially results in separate spatial patterns of binding to colonic dysplasia. The wavelength of emission planes is as follows: 520–560 nm (five planes, 10 nm scan step), 600–640 nm (five planes, 10 nm scan step) and 690–720 nm (four planes, 10 nm scan step). The composite unmixed images of single-probe-treated polyp showed respective signal under the excitation with band-pass filter of 480/30 nm for green, 540/25 nm for red and 679/41 nm for skyblue pseudocolor and triple-probe-treated polyp showed all positive signal under all excitation light.