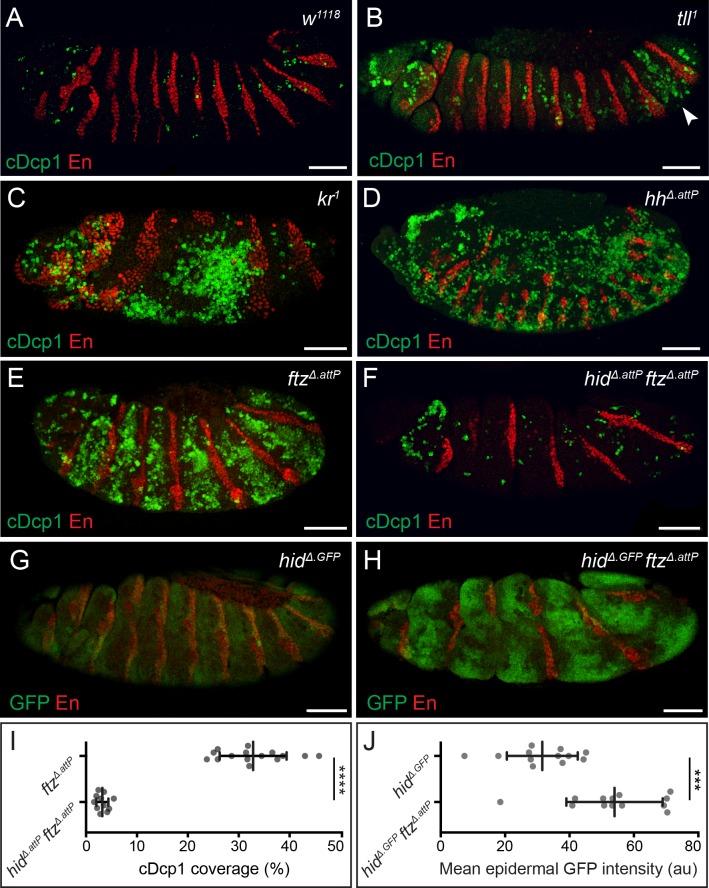
Fig 1. Widespread apoptosis in segmentation mutants is mediated by hid.
(A–E) cDcp1 immunoreactivity (green), in control (A), tll (B), kr (C), hh (D), and ftz (E) stage 13/14 embryos. Segmental enrichment of cDcp1 is detected around the regions where the mutated gene is known to act during normal development. Arrowhead in B indicates the zone of elevated Dcp1 cleavage in the posterior epidermis of tll1 embryos. Anti-Engrailed (En, red) provides a positional reference along the A/P axis throughout. (F) Epidermal cDcp1 immunoreactivity in stage 13 hidΔ.attP ftzΔ.attP double homozygotes is strongly reduced. (G, H) Transcription of hid, as assayed with the hidΔ.GFP reporter, is detected at uniform low levels in a wild-type background (G) but is up-regulated in a banded pattern in hidΔ.GFP ftzΔ.attP double homozygotes. Embryos late stage 12. Scale bars 50 μm. (I) Quantification of cDcp1 levels in ftzΔ.attP single mutant and hidΔ.attP ftzΔ.attP double mutant embryos. (J) Quantification of mean epidermal GFP intensity values throughout the epidermis of hidΔ.GFP single mutant and hidΔ.GFP ftzΔ.attP double mutant embryos. In graphs, means are shown, and error bars display standard deviation (****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, unpaired Student t test). The underlying data for (I) and (J) can be found in S1 Data. A/P, anterior/posterior; cDcp1, cleaved Death caspase-1; ftz, fushi-tarazu; GFP, green fluorescent protein; hh, hedgehog; hid, head involution defective; kr, krüppel; tll, tailless.