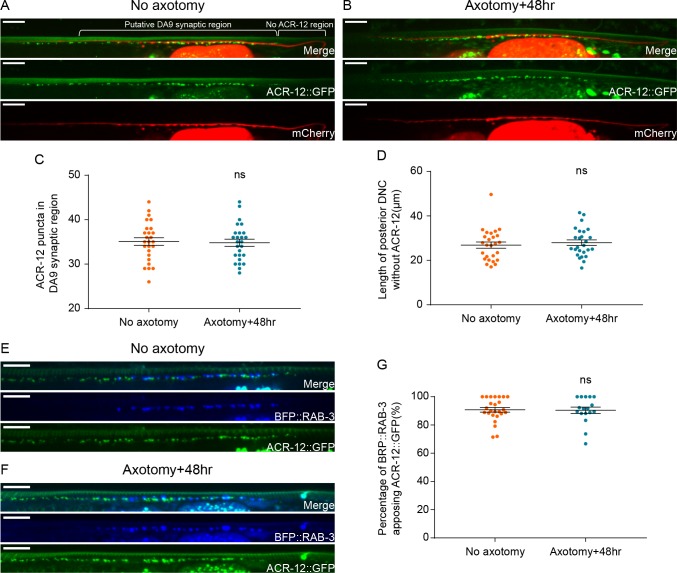
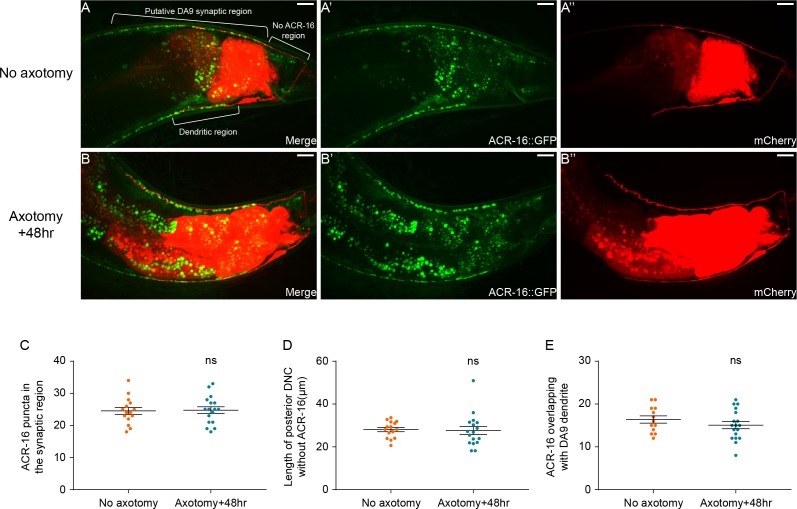
Figure 3. Postsynaptic receptors to DA9 maintain their localization and are aligned with DA9 SV clusters after axotomy.
(A) Labeling of DA9 axon and ACR-12 in GABA motor neurons in intact animals (2d old adults). Scale bars = 10 μm. (B) Labeling of DA9 axon and ACR-12 in GABA motor neurons in axotomized animals. Scale bars = 10 μm. (C) ACR-12::GFP puncta number in the putative DA9 synaptic region (~85 μm anterior from the most posterior ACR-12 puncta in the dorsal nerve cord) in both intact and axotomized animals. ns, not significant. Unpaired t test. (D) Length of posterior DA9 axon without ACR-12 in both intact and axotomized animals. ns, not significant. Unpaired t test. (E) BFP::RAB-3 puncta in DA9 axon appose ACR-12::GFP puncta in the postsynaptic GABA motor neurons in intact animals. Scale bars = 10 μm. (F) BFP::RAB-3 puncta in DA9 axon appose ACR-12::GFP puncta in the postsynaptic GABA motor neurons 48 hr after axotomy. Scale bars = 10 μm. (G) Percentage of BFP::RAB-3 apposing ACR-12::GFP in intact and axotomized animals. ns, not significant. Unpaired t test.