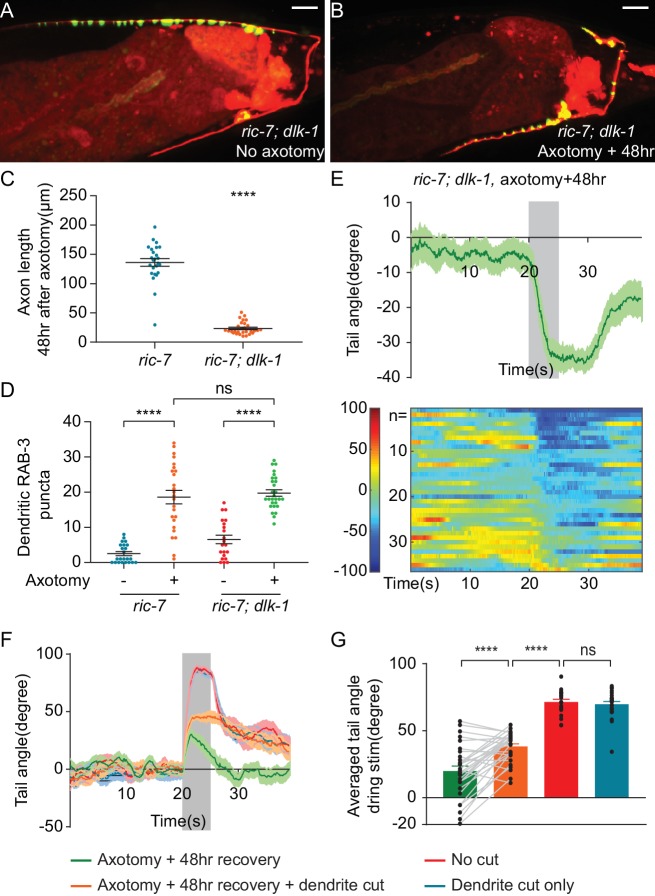
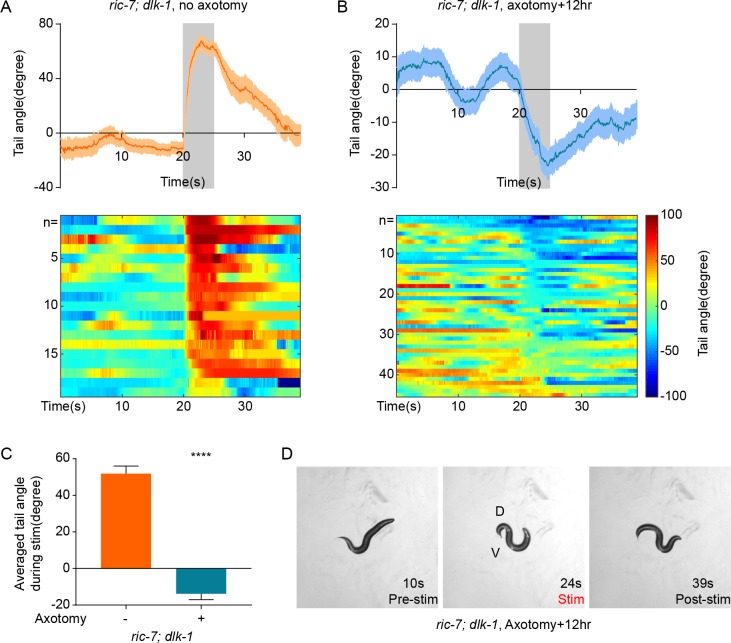
Figure 6. Aberrant information transfer is independent of dlk-1 and suppresses behavioral recovery.
(A and B) GFP::RAB-3 and mCherry labeling of DA9 in intact and axotomized ric-7(n2657); dlk-1(ju476) animals 48 hr after axotomy. Scale bars = 10 μm. (C and D) Comparison of length of regenerating axons (C) and number of dendritic RAB-3 puncta (D) between ric-7(n2657) and ric-7(n2657); dlk-1(ju476) animals 48 hr after axotomy. Mean ± SEM. ****p<0.0001; ns, not significant. Unpaired t test. (E) Ventral tail-bending behavior of ric-7(n2657); dlk-1(ju476) animals 48 hr after axotomy. The shaded area indicates the 5 s light stimulation. Mean ± SEM. (F) Traces of tail-bending behavior of ric-7(n2657) intact (red) and axotomized animals (green) 48 hr after axotomy. Dendrites of axotomized (orange) and intact animals (blue) were then cut and behavior was measured 2 hr later. Mean ± SEM. The shaded area indicates the 5 s light stimulation. (G) Averaged tail angles during stimulation of the animals in (F). Mean and SEM. ****p<0.0001; ns, not significant. Paired t test between green and orange. Unpaired t test between orange, red and blue.