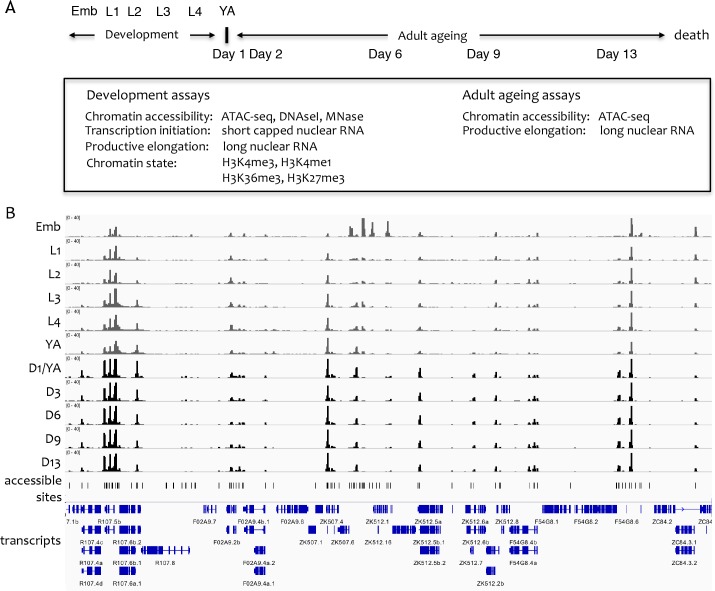
Figure 1. Overview of the project.
(A) Overview of genome-wide assays and time points of developmental and ageing samples. For development samples, chromatin accessibility, transcription initiation, productive elongation, and chromatin state were profiled in six stages of wild-type animals (embryos, four larval stages, young adults). For ageing samples, chromatin accessibility and productive transcription elongation were profiled in five time points of sterile adult glp-1 mutants (Day 1/Young adult, Day 2, Day 6, Day 9, Day 13). (B) Representative screen shot of normalized genome-wide accessibility profiles in the eleven samples (chrIII:9,041,700–9,196,700, 154 kb).