TABLE 2. Criteria for QRSd Measurement Algorithm Steps.
| Step | Action | Parameter | Value/Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prior to QRSd algorithm | Removal of array-specific outliers | Morphological features | Cross-correlation |
| Peak polarities, magnitudes, and temporal position | |||
| Exclusion criteria | Channel is morphologic outlier in the first, middle, and last PM complex | ||
| 6. | Identification of peak bounds | Leading or trailing peak boundary | Earlier of zero-crossing and concavity change |
| Significance assessment | Order of candidate peak evaluation | In order of ascending proximity to the reference peak | |
| Peak significance criteria | Peak position | Occurs after preceding significant peak bounds | |
| Peak amplitude | Opposite polarity of preceding significant peak | ||
| Criteria scaling factor | Ratio of candidate peak height to reference peak height | ||
| Leading and falling phase slope | Reference peak slope 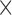 scaling factor scaling factor |
||
| Leading and falling phase curvature | Reference peak curvature 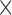 scaling factor scaling factor |
||
| 7. | Removal of array-specific peak outliers | Maximum peak-to-peak spacing | 52 ms A |
| 8. | Delineation of channel specific borders | Amplitude | <50% of the height of the closest significant peak |
| Slope | <2.5 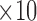 −2 mV/ms B −2 mV/ms B
|
||
| 9. | Delineation of array-specific borders | Group of normal array-specific border values | Largest group of borders within 20-ms |
| Array-specific start | Earliest in the group of array-specific normal start values | ||
| Array-specific end | Latest in the group of array-specific normal start values | ||
| 10. | Delineation of global borders | Global start | Earlier of the array-specific start values |
| Global end | Later of the array-specific end values |
Based on precision of 12-lead ECG grid paper
Based on difference (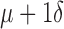 ) between paired global and widest single-lead 12-lead ECG QRSd measurements (n = 150)
) between paired global and widest single-lead 12-lead ECG QRSd measurements (n = 150)
Criteria without sources were determined during the development process
