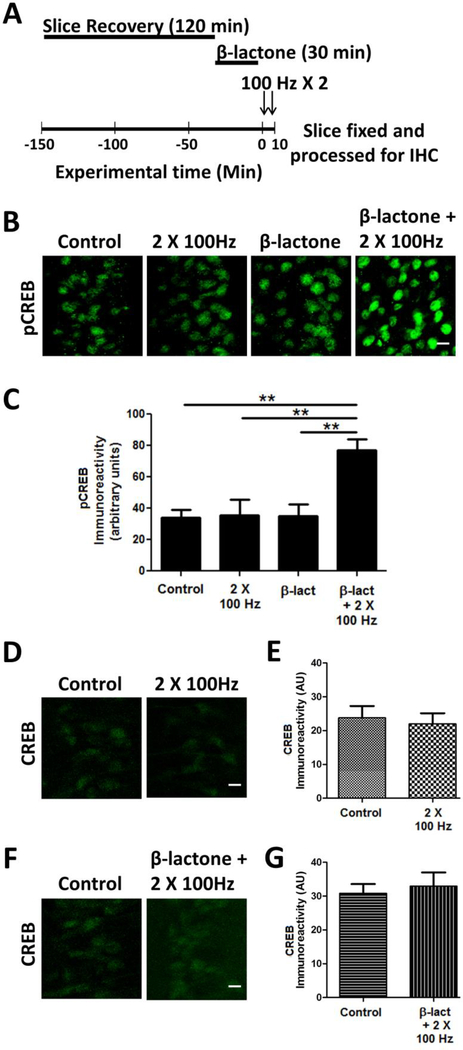
Figure 1.
β-lactone treatment increases CREB phosphorylation (pCREB).
(A) Schematic outline of the experiment: after the recovery period of 120 min, hippocampal slices were treated with β-lactone for 30 min. The beginning of electrophysiological stimulation is designated as 0 min at which point the slices were subjected to subthreshold LTP induction (2 × 100 Hz). (B) Confocal images of pCREB immunoreactivities in the CA1 region of hippocampal slices without any treatment (control) or after subthreshold LTP induction (2 × 100 Hz) alone, after β-lactone treatment alone, after β-lactone treatment followed by subthreshold LTP induction (β-lactone + 2 × 100 Hz). Scale bars: 20 μm. (D) Quantification of pCREB immunoreactivities shows that β-lactone treatment significantly increases CREB phosphorylation. (D) CREB immunoreactivities in the CA1 region with no treatment (control) or after subthreshold LTP induction (2 × 100 Hz). (F) CREB immunoreactivities in the CA1 region with no treatment (control) or after β-lactone treatment followed by subthreshold LTP induction (β-lactone + 2 × 100 Hz). (E, G) Quantification of CREB immunoreactivities of results shown in panels D & F. **p<0.01 comparison between two groups as indicated by horizontal lines.