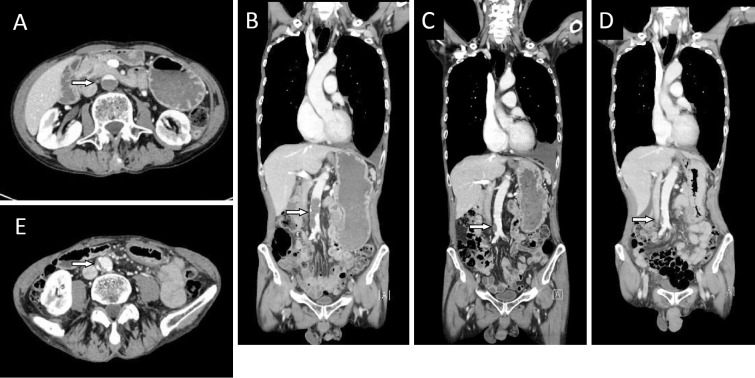
Figure 2.
A: CT (axial view) after 2 courses of bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy showed that the abdominal aortic artery was almost occluded by a newly formed thrombus (arrow) from the level below the renal arteries to the common iliac arteries. B: CT (coronal view) at the same time of 2A demonstrated the newly formed thrombus (arrow). C: After heparin and warfarin therapy, the size of the aortic arterial thrombus (arrow) was reduced. Increased left pleural effusion was found. D: A small mural thrombus with calcification in the abdominal aorta was noted on imaging obtained before the initiation of bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy (arrow). E: CT (axial view) before the initiation of chemotherapy showed a mural thrombus (arrow).