Figure 5. Hydrogel implantation for non-invasive pH sensing in vivo.
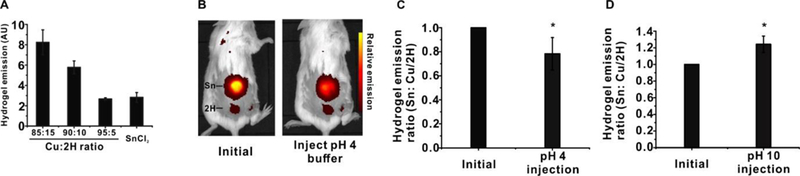
A) Fluorescence emission of Cu:2H blended porphyrin hydrogels (non pH-responsive) relative to tin ones (pH-responsive). B) Fluorescent images of living mice with an implanted tin hydrogel (top) and Cu:2H hydrogel (bottom), pre- and post- subcutaneous injection with pH=4 100 mM sodium phosphate. Relative transdermal fluorescence emission ratios of tin and Cu:2H hydrogels in mice implanted with hydrogels before and after injection with C) pH=4 and D) pH=10 phosphate solutions. Data show mean +/− std. dev. for n=3 separate mice, * indicates a statistically significant change based on a two-tailed student’s t-test (p<0.01).
