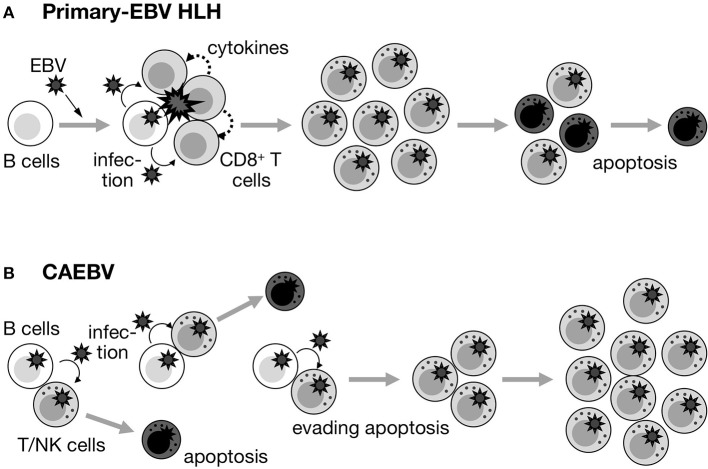
Figure 2.
Fate of EBV+ T/NK cells in primary-EBV HLH and CAEBV. (A) Primary-EBV HLH. EBV-infected T/NK cells may transiently proliferate under specific conditions (primary EBV infection and large amounts of cytokines). However, they maintain a proapoptotic nature, and may be induced to enter apoptosis by themselves, steroids/CsA, and/or anti-cancer drugs. (B) CAEBV. Although EBV occasionally infects T/NK cells, EBV-infected T/NK cells inherently have pro-apoptotic effects and repeatedly appear and disappear. However, some of these cells acquire a self-maintaining and self-expanding predisposition over the course of years and contribute to the development of disease.