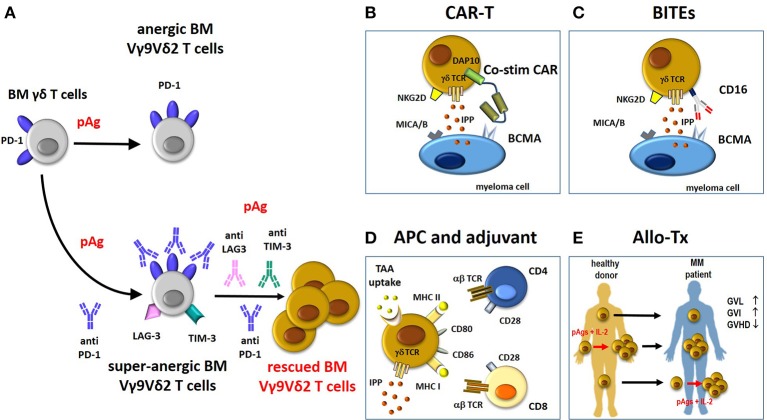
Figure 2.
Potential contribution of rescued Vγ9Vδ2 T cells to immune treatments in MM. (A) BM Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in the TME are PD-1+ and anergic to pAg-stimulation. This anergy is not overcome by pAg stimulation in the presence of anti-PD-1. Paradoxically, the pAg + anti-PD-1 combination deepens the anergy of BM MM Vγ9Vδ2 T cells (super-anergic state). One possible hallmark of super-anergic immune effector cells is the expression of multiple ICP (i.e., LAG-3. TIM-3) on the same cells. Combinations of multiple anti-ICP antibodies (anti-PD-1/anti-LAG3/anti-TIM-3) is necessary to overcome the super-anergic state. If rescued from the anergic or super-anergic state, Vγ9Vδ2 T cells can become attractive candidates for immune interventions as proposed in panels B-E. Compared to conventional T cells, Vγ9Vδ2 T cells are not MHC-restricted and can be activated by pAgs (IPP), and stress-induced self ligands (i.e., MICA/B) other than CARs, tumor-specific transferred αβ TCR genes, and BITEs (see also text). (B) The “costimulatory only” CAR Vγ9Vδ2 T cells approach (58). In these cells, the cytotoxic capacity of CD3 (signal 1) is mediated through the native γδ-TCR recognition of IPP, whereas costimulation (signal 2) is provided by a CAR recognizing BCMA with an endodomain consisting of the innate NKG2D signaling molecule, DAP10. The cytotoxic ability of CAR Vγ9Vδ2 T cells is improved by the recognition of other molecules expressed by myeloma cells like MICA/B via NKG2D. (C) BITEs can be used to re-direct CD16-expressing Vγ9Vδ2 T cells against MM antigen (i.e., BCMA) and enhance their cytotoxic anti-tumor activity. (D) Vγ9Vδ2 T cells can act as APC to present TAA to MHC-restricted CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. APC-Vγ9Vδ2 T cells express many APC-related cell surface receptors like MHC-I and II, and co-stimulatory proteins (CD80, CD86). (E) The beneficial activity of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in the allo-tx settings can be exploited as follows: i) direct infusion of unmanipulated grafts containing small amounts of donor circulating Vγ9Vδ2 T cells; these cells can increase in number after infusion depending on several factors like infections etc; (ii) donor Vγ9Vδ2 T cells from healthy donors are expanded ex-vivo before reinfusion in graft recipients using pAg like zoledronic acid and IL-2 (73); (iii) donor Vγ9Vδ2 T cells are expanded in vivo in the recipient after allo-tx with pAgs like zoledronic acid and IL-2. BM, bone marrow; pAg, phosphoantigen; CAR-T, chimeric antigen receptor-T; co-stim-CAR, “costimulatory only” CAR; BITEs, bispecifc T-cell engager; APC, antigen-presenting cell; TAA, tumor-associated-antigen; allo-Tx, allogenic-transplantation; GVHD, graft-vs.-host disease; GVL, graft-vs.-leukemia; GVI, graft-vs.-infections; IL-2, interleukin-2.