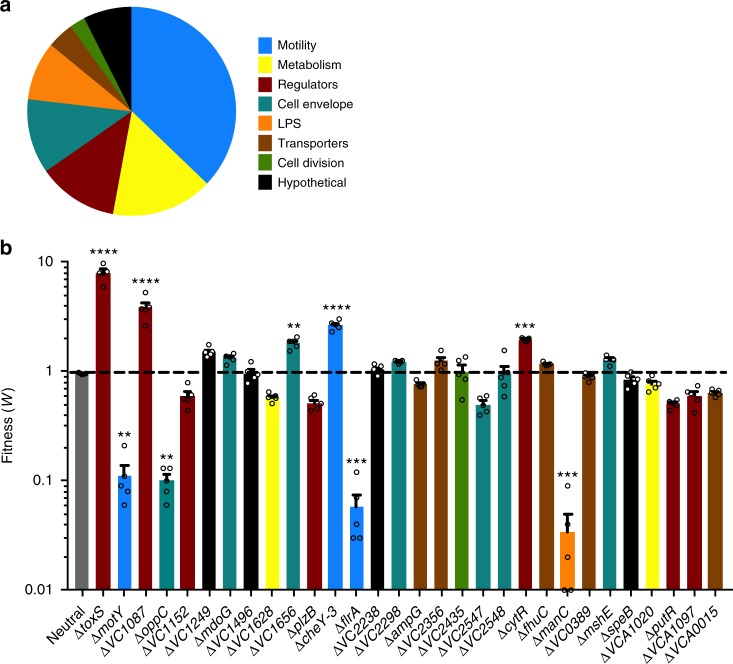
Fig. 1.
V. cholerae mutants with altered sensitivity to B. bacteriovorus predation. a We generated a complex V. cholerae transposon mutant library and subjected it to transposon-insertion sequencing (Tn-seq) before and after predation by B. bacteriovorus. Mutants with decreased fitness (w < 0.4) are shown and categorized according to gene ontology terms. b Promising transposon mutants identified in a were re-created by gene deletion and replacement with an FRT scar. This FRT scar served as a pseudo-transposon for a mini Tn-seq of a much smaller mutant library: 32 mutants compared to 50,000 in the initial Tn-seq. The color scheme of a matches b. The average fitness values and standard errors of the mean (SEM) for five biological replicates are shown. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Significance was determined by comparing the fitness of each mutant to the average fitness values for two neutral genes. **P < 0.002; ***P < 0.0007; ****P < 0.0001 (ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test)