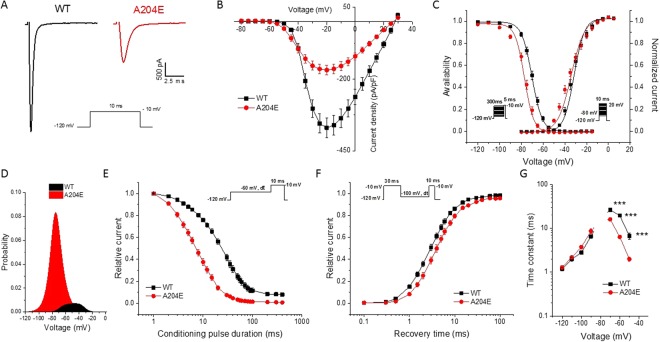
Figure 2.
Biophysical properties of wild-type (WT) and mutant A204E hNav1.4 channels in HEK293 cells. (A) Representative whole-cell current traces recorded from HEK293 cells expressing wild-type (WT, black) or A204E (red) hNav1.4 channels in response to a test pulse of 10 ms at −10 mV from a holding potential of −120 mV are shown. (B) Normalized current/voltage relationships of WT (n = 36) and A204E (n = 28) channels. Current densities were normalized by cell capacitance. (C) Voltage dependence of activation and steady-state fast inactivation curves for WT and A204E channels were plotted and fitted with a single Boltzmann equation. (D) Effect of A204E on window current. The probability of being within this window was calculated as indicated in the materials and methods section. (E) Steady-state fast inactivation for WT and A204E channels in response to the pulse protocol shown in the inset. (F) Recovery from fast inactivation of WT and A204E channels. (G) Voltage-dependence of time constants (τ) of fast inactivation for WT (n = 9) and A204E (n = 9) channels obtained when measuring entry from −70 to −30 mV and recovery from −120 to −80 mV. The statistical differences between WT and A204E channels are shown (***P < 0.001).