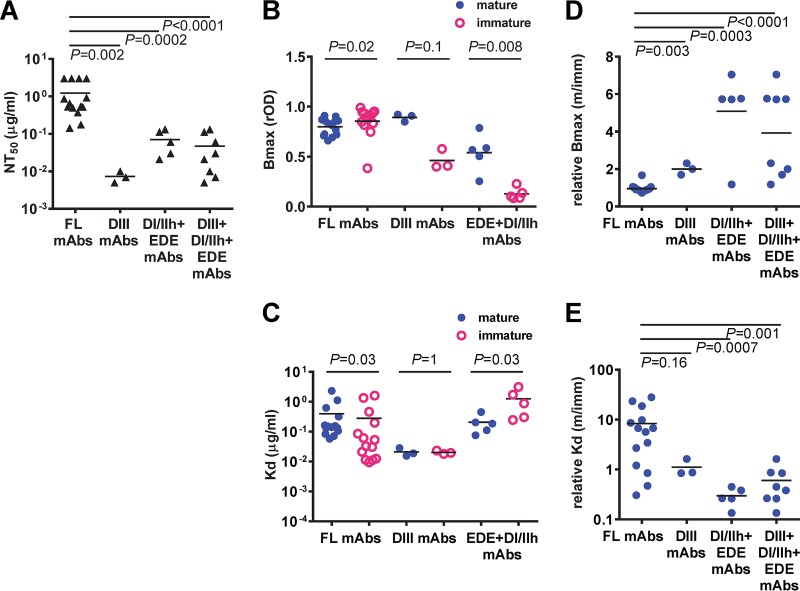
FIG 2.
Comparison of neutralizing potency, maximum binding, and dissociation constants of different categories of human anti-E MAbs to mature, immature, or mixed particles. (A) DIII, EDE, and DI/IIh MAbs were more potent neutralizers than FL-specific MAbs. (B, C) Comparison of the Bmax (B) and Kd (C) for mature or immature DENV1 particles within each category of MAbs, including FL, DIII, and EDE plus DI/IIh MAbs. (D, E) Comparison of the relative Bmax (D) and relative Kd (E) for mature versus immature DENV1 particles, Bmax (m/imm) and Kd (m/imm), respectively, between FL, DIII, and EDE plus DI/IIh MAbs. Bmax and Kd were determined by nonlinear regression analysis (GraphPad Prism software, version 6.0). Data are the means for duplicates from two experiments. P values were based on the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test.