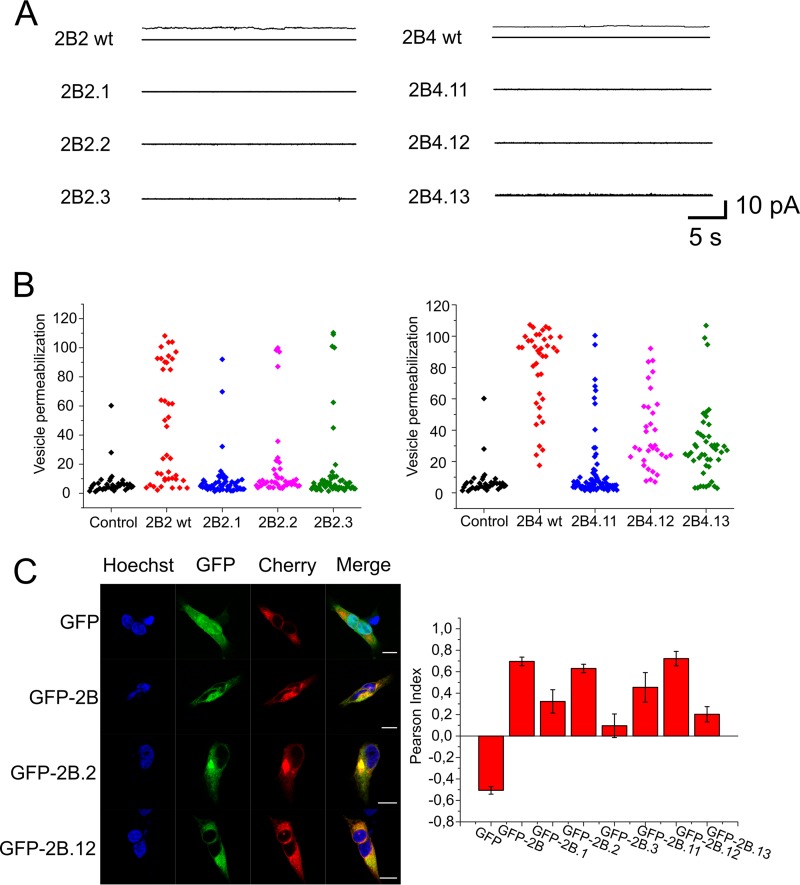
FIG 7.
Functional effects of lethal mutations targeting 2B2 and 2B4 transmembrane regions. (A) Current recordings in 150 mM KCl, at a potential of 50 mV, after addition to ER-like lipid bilayers of 2B2 or 2B4 peptide variants incorporating the mutations (recordings on the left and right, respectively). (B) Mean permeabilization values for ER-GUVs treated with 2B2 or 2B4 peptide variants (left and right, respectively). (C) Locations of native and mutated forms of 2B in the ER by confocal microscopy. Micrographs on the left illustrate individual cells coexpressing several GFP constructs and the ER marker mCh-Sec61. Control GFP (i.e., devoid of membrane anchors) labeled the complete cell but was excluded from the ER (top panels), whereas GFP-2B constructs were excluded from the nucleus and colocalized with mCh-Sec61. The panel on the right displays colocalization of mCh-Sec61 and GFP in the samples, including the different 2B mutants, as calculated with the ImageJ plug-in Coloc 2 (http://imagej.net/Coloc_2). Measurements were carried out in at least 6 cells, as for those displayed in the micrograph. Bars represent mean values ± standard errors (SEs). Maximal colocalization with mCh-Sec61 was observed for the fusions, including the 2B.WT protein and the 2B.2 and 2B.12 mutants.