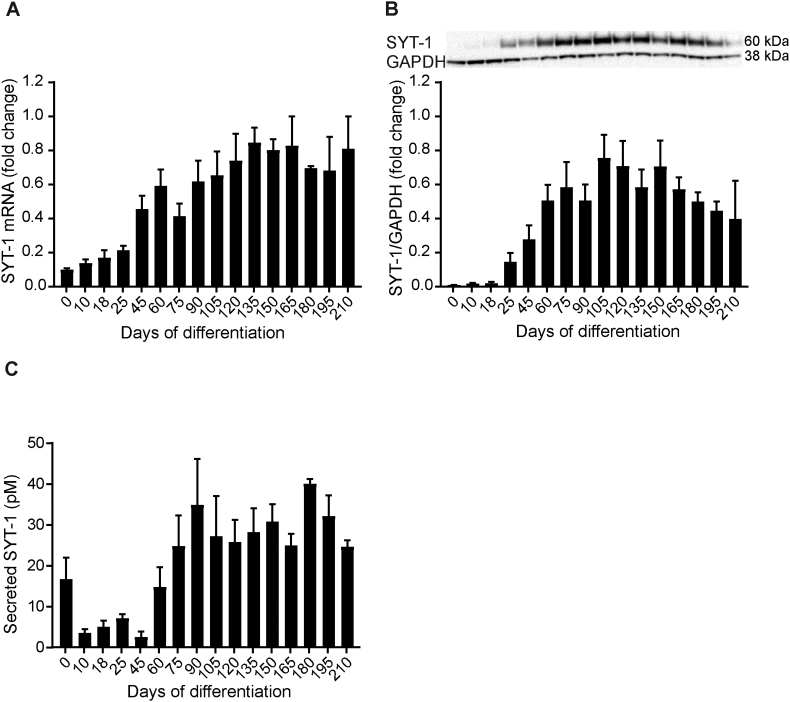
Fig. 5.
SYT-1 mRNA and protein expression during hiPSC differentiation to cortical neurons. (A)SYT-1 mRNA was detected by quantitative PCR and was first expressed on d0. There was a trend towards increased expression of SYT-1 mRNA between d0 and d165. SYT-1 mRNA levels were normalized to the average of HPRT-1, RPL-27 and RPL-30 genes and SYT-1 mRNA fold change in each differentiation was related to the highest SYT-1 mRNA expression, set to 1. For a summary of assigned significances for the measured changes of SYT-1 mRNA, see Supplementary Table 7. (B) SYT-1 protein levels were detected by western blot and were not observed until d18 of differentiation. Thereafter, there was a gradual increase in SYT-1 levels until d105, when expression was the highest. After d150, SYT-1 levels decreased. SYT-1 protein levels were correlated to GAPDH and SYT-1 fold change in each differentiation was related to the highest SYT-1 protein level, set to 1. Representative bands of SYT-1 and GAPDH are shown. The summary of assigned significances for the measured changes of SYT-1 protein is shown in Supplementary Table 8. (C) Secreted SYT-1 was detected by immuno-precipitation (IP) followed by parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) mass spectrometry; the assay targets mainly the SYT-1 C2A calcium binding domain. Fig. 4C show that SYT-1 was secreted at high concentrations on d0. The secreted SYT-1 decreased remarkably from d0 until d45. Thereafter, SYT-1 secretion increased gradually from d60 to d90. After d180, there was a trend towards decreased secretion of SYT-1. The summary of assigned significances for the changes of secreted SYT-1 concentration is summarized in Supplementary Table 9. Bars represent mean±SEM. For intracellular expression of SYT-1 mRNA and protein, n = 4 (except from d165 to d210 where n = 2) and secreted SYT-1, n = 5 (except from d165 to d210 where n = 3).