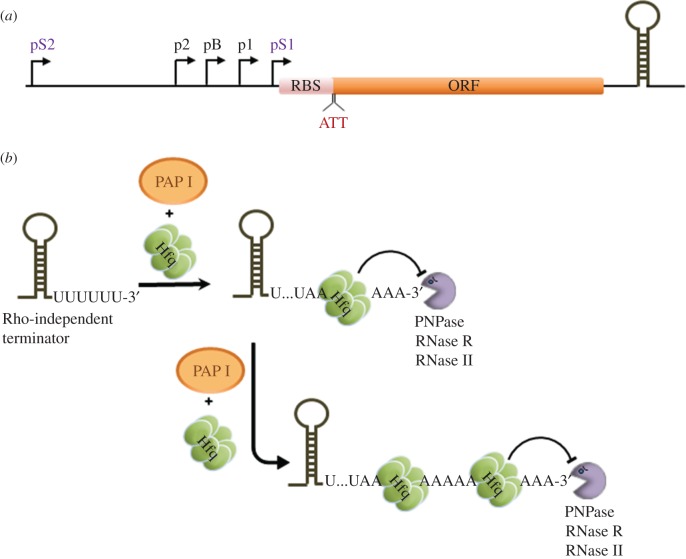
Figure 2.
Control of poly(A) polymerase I level and activity in E. coli. (a) Control of E. coli pcnB expression. Transcription of the pcnB gene coding for PAP I is driven by three σ70-dependent (i.e. p1, pB and p2) and two σS-dependent (pS1 and pS2) promoters [46]. Moreover, ppGpp and DksA were found to directly inhibit transcription from pB, pS1 and pS2 and the overall low level of PAP I is maintained owing to lower efficiency of translation caused by the presence of a non-canonical start codon (AUU) within the ribosome-binding site (RBS). (b) Effect of Hfq on poly(A) addition. The RNA chaperone Hfq can bind to poly(A) tails, thereby impeding their exonucleolytic degradation and concomitantly increasing the processivity of the poly(A) addition by PAP I. ORF, open reading frame. (Online version in colour.)