Figure 4.
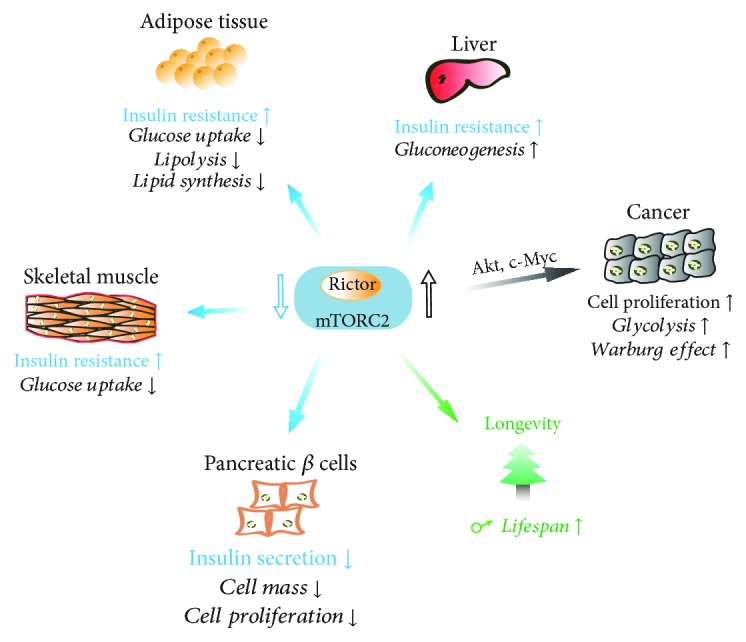
Impact of mTORC2-mediated metabolism on T2DM, cancer, and aging. In T2DM, the suppression of mTORC2 leads to gluconeogenesis in the liver and impaired glucose uptake in the muscle and adipose tissue, leading to insulin resistance. In pancreatic β cells, mTORC2 dysfunction also leads to reduced β-cell mass, proliferation, and impaired insulin secretion. In many types of cancers, mTORC2 activation promotes glucose uptake and glycolysis, which may contribute to the altered glucose metabolism and Warburg Effect, which fuels cell proliferation. In mammals, mTORC2 activity promotes longevity in males without established mechanism.
