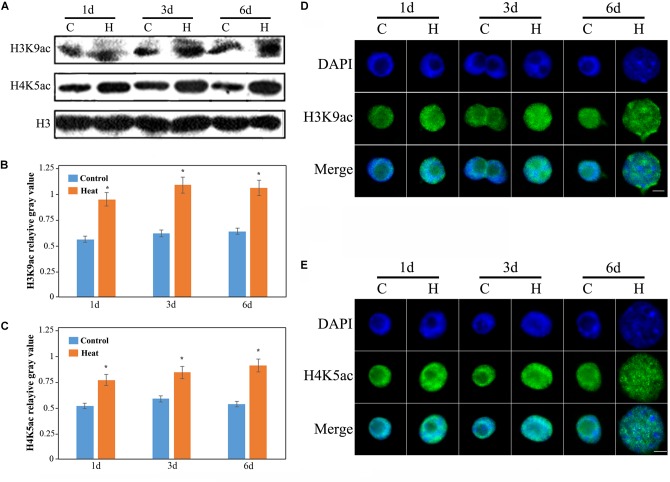
FIGURE 2.
Histone acetylation showed an increasing trend in the heat-induced inhibition of lateral root initiation in maize seedlings. (A) The levels of H3K9ac and H4K9ac in the roots of maize seedlings increased significantly under heat treatment. All the western blot assay were repeated three times, and histone H3 was used as the standard internal reference. (B) The mean gray value of H3K9ac bands. (C) The mean gray value of H4K5ac bands. (D) Immunological staining indicated an increase in the acetylation level of H3K9. (E) Immunologic staining showed an increase in the acetylation level of H4K5. The level of histone acetylation in the lateral root development of maize seedling was increased, and the nucleus was decondensed. Five hundred nuclei were observed in each sample. The Bar = 10 μm. Asterisk (∗) indicated that the gene expression level of the heat treatment group which was found to be significantly different from that of the control group (t-test, p < 0.01).