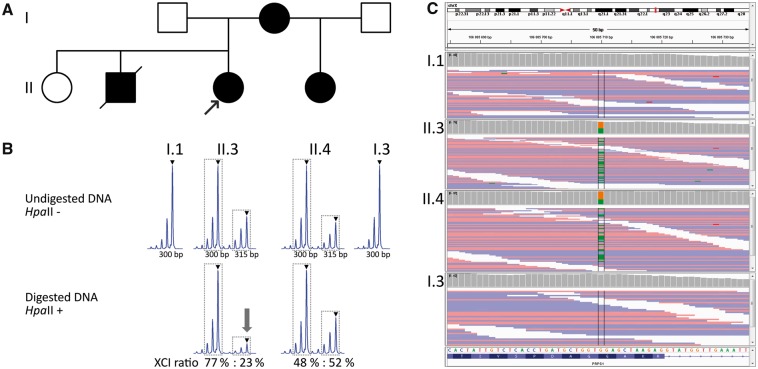
Fig. 1.
Genetic studies
(A) Family pedigree. Black symbols denote affected individuals and open unaffected individuals. (B) X-inactivation analysis in the proband (II.3) and her half-sister (II.4). The XCI ratio was calculated as the ratio of the peak areas of two alleles of the analysed polymorphic repeat in the digested sample, and the result was corrected by the ratio of the peak areas of two alleles in the undigested sample to avoid an error caused by preferential amplification of the shorter allele. The main peaks are denoted by triangle; peak areas used in the X-inactivation ratio formula are designated by dotted lines. The arrow highlights the evident reduction of the maternal allele in the digested sample. (C) The integrative genome viewer (IGV) displays heterozygous mutation chrX: 106885710 NM_002764; c. G>A; p.G174R) of PRPS1 in affected individuals II.3 and II.4 and normal genotype in their fathers I.1 and I.3. XCI: X-chromosome inactivation; chrX: chromosome X.