FIGURE 2:
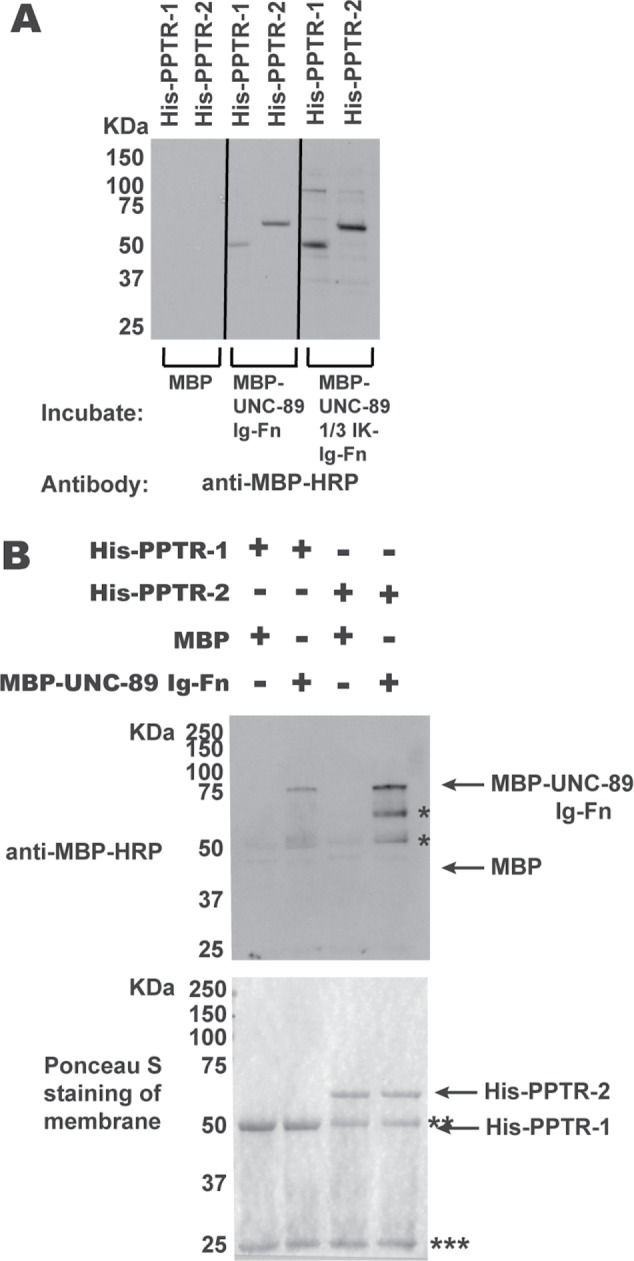
Segments of UNC-89 interact with PPTR-1 and PPTR-2 in vitro. (A) Far-Western assay. His-tagged PPTR-1 and PPTR-2 were separated by SDS–PAGE, transferred to membrane, incubated with MBP, MBP-UNC-89 Ig53-Fn2, or MBP-UNC-89 1/3 IK-Ig53-Fn2, washed, incubated with anti–MBP-HRP, washed, and detected by ECL. Both MBP fusions of these portions of UNC-89, but not MBP itself, bind to either His-PPTR-1 or His-PPTR-2. (B) In-solution pull-down assay. The indicated proteins were incubated together, and then the His-tagged proteins were pelleted using anti-6His beads. Proteins were eluted from the beads and separated by SDS–PAGE and transferred to a membrane, and then a Western blot was performed using anti–MBP-HRP to detect any copelleting MBP or MBP-UNC-89-Ig-Fn. At the bottom is shown the blot after Ponceau S staining, and above it is the Western blot. Both His-PPTR-1 and His-PPTR-2 pull down MBP-UNC-89-Ig-Fn, but not MBP. Positions of proteins are indicated by arrows; * likely degradation products from MBP-UNC-89-Ig-Fn; ** Ig heavy chain; *** Ig light chain. The predicted molecular weights of the bacterially expressed purified proteins are as follows: His-PPTR-1, 51.5 kDa; His-PPTR-2, 60 kDa; MBP, 42.5 kDa; MBP-UNC-89 Ig53-Fn2, 73.5 kDa; and MBP-UNC-89 1/3 IK-Ig53-Fn2, 97.3 kDa.
