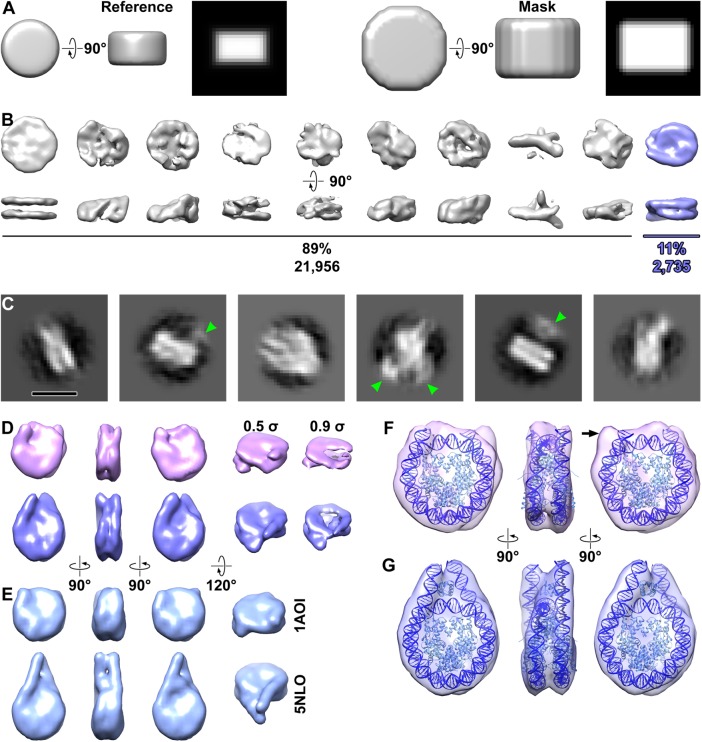
FIGURE 2:
Structural analysis of nucleosomes in situ. (A) The reference model (left half) and mask (right half) used for three-dimensional classification and averaging. The reference is 10 nm wide and 6 nm thick. Both the reference and mask have soft edges that slowly decay to zero. The rightmost subpanel (black background) for both the reference and mask are central slices through the side view. (B) Three-dimensional class averages of all template-matching hits. The nucleosome class average (blue) is oriented with its twofold dyad axis running horizontal. (C) Example two-dimensional class averages from the nucleosomes identified by three-dimensional classification. Some of the class averages have densities from nucleosome-associated complexes (green arrowheads). Bar, 10 nm. (D) Final three-dimensional class averages of nucleosomes, showing from left to right the front, side, and back and oblique views. One class (39%, magenta) has shorter linker-DNA densities that the other (61%, blue). Maps in all columns are contoured at 0.5 σ except in the rightmost column, which is set to 0.9 σ to better show the left-handed superhelical DNA path and the degree of linker-DNA heterogeneity. (E) Crystal structures of the nucleosome core (PDB 1AOI, top) and chromatosome (PDB 5NLO, bottom), rendered as 15-Å resolution density maps. (F, G) Refined maps of the two nucleosome classes, with the edited chromatosome crystal structure docked (F) without or (G) with the linker histone, and linker DNA appropriately truncated. The histones and DNA are light and dark blue, respectively.