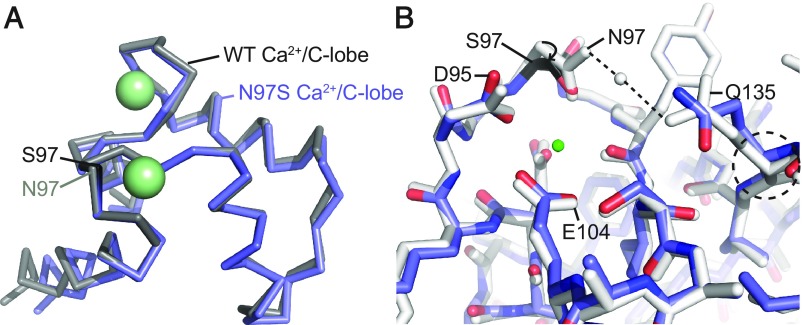
Fig. 3.
Comparisons of the wild-type Ca2+/CaM and N97S Ca2+/CaM structures. (A) Overall superposition of the C-lobes of wild-type Ca2+/CaM (PDB ID code 4BW8, gray) and N97S Ca2+/CaM (blue). C-lobes are shown in ribbon representation and calcium ions as green spheres. S97 is colored black. (B) Superposition of wild-type Ca2+/CaM (gray) and N97S Ca2+/CaM (blue) based on residues 92–102; shown are details around EF3. CaM is in stick representation, with the mutated S97 residue in black, and calcium ion as a green sphere. The dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. To maintain a similar Ca2+-coordination, the main chain and side chain of Ser97 move closer, likely resulting in strain that reduces the Ca2+ affinity. Due to the absence of hydrogen bonds with Gln135 in the mutant, the Gln135 conformation is altered, resulting in small changes in EF4.