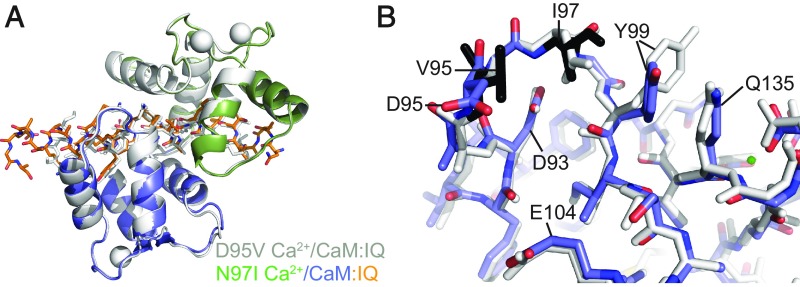
Fig. 4.
Comparison of the D95V Ca2+/CaM - and N97I Ca2+/CaM:CaV1.2 IQ domain structures. (A) Superposition of D95V Ca2+/CaM:IQ (gray) and N97I Ca2+/C-lobe:IQ (N-lobe in green, C-lobe in blue, IQ in orange) based the IQ domain. CaM is shown in cartoon representation, IQ domain as sticks, and calcium ions as spheres. The overall conformation of N97I is similar to D95V, and thus very different from wild-type Ca2+/CaM. (B) Superposition of D95V Ca2+/CaM (gray) and N97I Ca2+/CaM (blue) based on residues 92–102; shown are details around EF3. CaM is in stick representation, with the mutated residues in black, and calcium ion as a green sphere. In both mutants, no Ca2+ is visible in EF3, leading to a conformational switch, mediated by Glu104. A noticeable difference is the stacking of Tyr99 against the hydrophobic Ile97 residue. This conformation of Tyr99 is unique, and not found in wild-type Ca2+/CaM or any of the other disease mutant structures. Because Tyr99 now stacks against EF4, small changes in the positions of EF4 residues can be observed.