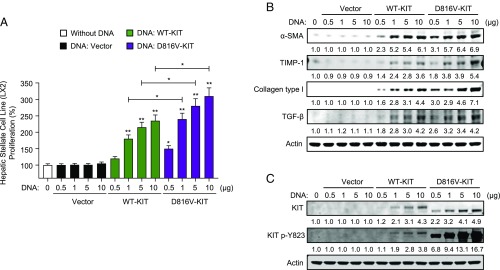
Fig. 5.
Enforced expression of WT-KIT or D816V-KIT induces HSC proliferation and differentiation. (A) Proliferation and (B) differentiation of HSCs transfected with the indicated amounts of plasmids containing WT-KIT or D816V-KIT. Two days after transfection, cells were plated in 24-well plates for 24 h. Cell proliferation was measured using an MTT assay (A) and changes in markers of differentiation analyzed by Western blots (B). Data in A are mean ± SEM, and the numbers underneath each band in B represent average fold changes in fluorescence intensity normalized to actin and compared with the band intensity of untreated cells (n = 3) (SD was <10% of the average). (A) *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01, compared with the corresponding vector control or as indicated by the bar. (C) Levels of KIT expression and KIT phosphorylation in the same samples are shown for each concentration of plasmid DNA. Note that enforced expression of D816V-KIT results in different mobility in SDS/PAGE, which has been documented in some cells and can be attributed to abnormal glycosylation and/or ubiquitinylation of the mutated receptor (44, 59).