Fig. 5.
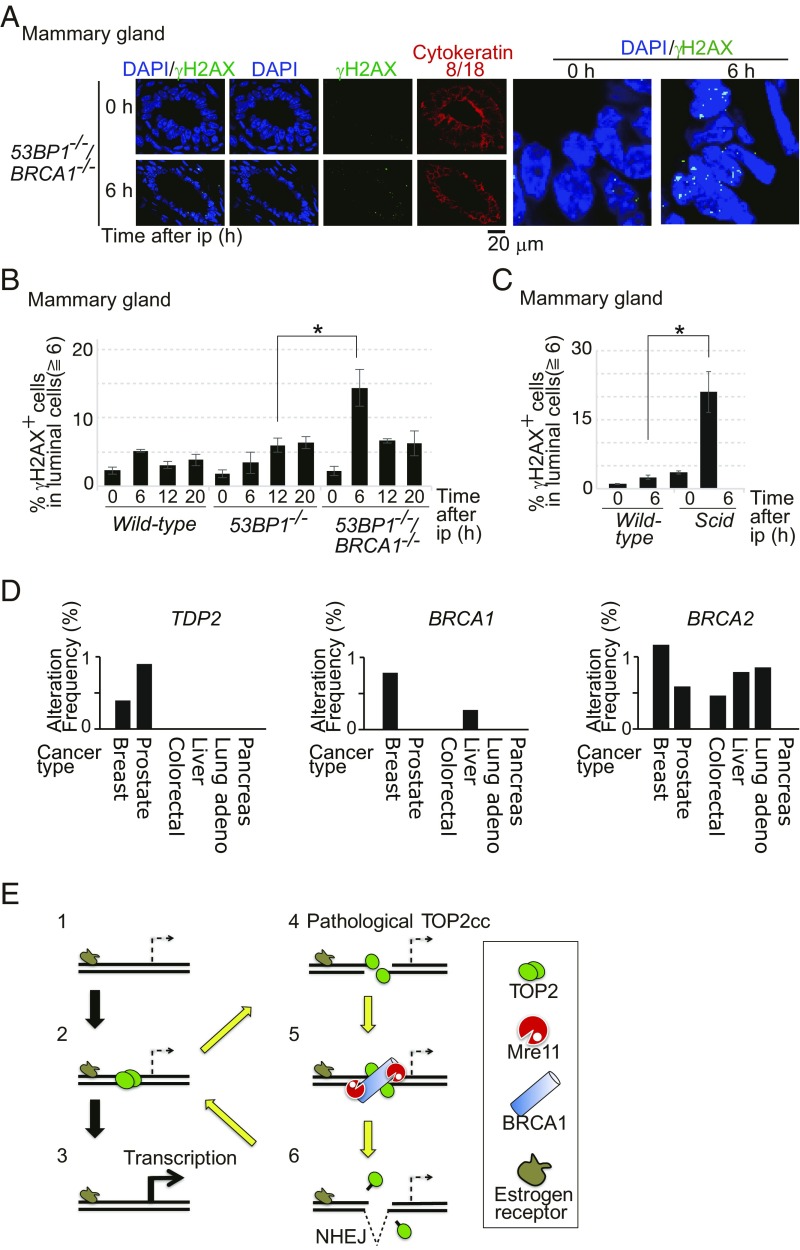
E2 is genotoxic to luminal epithelial cells of mammary glands in mice deficient in BRCA1 or NHEJ. (A) E2 was given to 53BP1−/−/BRCA1−/− mice via i.p. injection. Mammary-gland tissues were isolated at 0 and 6 h after ip, and immunostained with α-γH2AX and α-cytokeratin 8/18 antibodies. Luminal cells, which express the ER, were stained with α–cytokeratin-8/18. (A, Right) Images indicate enlarged view of γH2AX foci (green) on luminal cells. (B) Percentage of γH2AX focus-positive cells in luminal epithelial cells at the indicated time after ip with E2. For a wild-type strain relevant to 53BP1−/− and 53BP1−/−/BRCA1−/− mice, the C57BL6/J strain was used. Representative images of γH2AX foci are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S10A. The asterisk indicates P < 0.02, calculated by Student’s t test. (C) Data are shown as in B. For a wild-type strain relevant to NHEJ-deficient Scid mice, the C.B.-17/lcr strain was used. The asterisk indicates P < 0.01, calculated by Student’s t test. (D) The search of TCGA database indicates that homozygous deep deletion of the TDP2 gene is found in breast-invasive cancers and prostate cancers but not other types of malignant cancers. The y axis shows the percentage of the indicated cancers carrying homozygous deep deletion of either TDP2, BRCA1, or BRCA2 in 818 breast-invasive (50), 333 prostate (53), 212 colorectal (51), 373 liver (TCGA, provisional), 230 lung (52), and 150 pancreas (TCGA, provisional) cancer samples, registered in TCGA database. Homozygous deep deletion of the TDP2 gene is observed in three cases of the 818 breast-invasive and three cases of the 313 prostate cancer samples, but in neither the colorectal, liver, lung, nor pancreas cancer samples. (E) Proposed model for the effect of E2 on TOP2cc formation in an ER target gene. Exposure of cells to E2 translocates the ER to target genes (step 1) and triggers the transient formation of TOP2ccs in transcriptional regulatory sequences (step 2). Some ER target genes require TOP2-mediated catalysis for their transcriptional control (step 3). Occasional abortive catalysis of TOP2 causes the formation of pathological TOP2ccs, including DSBs covalently associated with the degradative products of TOP2 (step 4, yellow arrow). BRCA1 promotes the recruitment of MRE11 to pathological TOP2cc sites (step 5). MRE11 as well as TDP2 removes TOP2 and its degradative products from DSB ends for subsequent ligation by NHEJ (step 6) in G0/G1 phase.