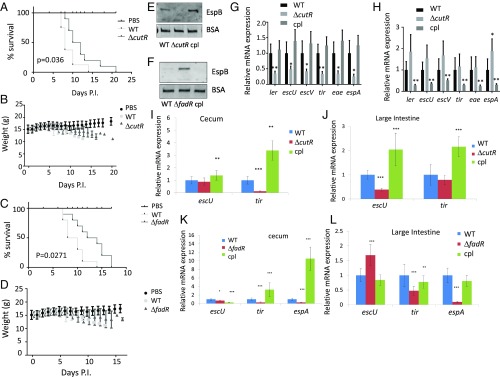
Fig. 2.
Representative screen hits in C. rodentium pathogenesis. All experiments were conducted using conventional mouse feed. Survival curves of C3H/HeJ infected with 109 cfu of WT, (A) ΔcutR, or (C) ΔfadR DBS770 C. rodentium or with PBS control (10 animals per infection group and 8 animals for PBS). Statistical significance calculated by Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test. Weight of animals infected with (B) ΔcutR, or (D) ΔfadR DBS770, WT or mock (PBS). (E) Western for EspB from in vitro culture supernatants from WT, ΔcutR DBS770 and ΔcutR complemented (cultures grown in DMEM). (F) Western for EspB from in vitro culture supernatants from WT, ΔfadR DBS770, and ΔfadR complemented (cultures grown in DMEM). (G) qRT-PCR of C. rodentium LEE mRNAs from in vitro anaerobically grown WT, ΔcutR DBS770, and ΔcutR complemented strains (cultures grown in DMEM). (H) qRT-PCR quantification of C. rodentium LEE mRNAs from in vitro anaerobically grown WT, ΔfadR DBS770, and ΔfadR complemented strains (cultures grown in DMEM). (I) qRT-PCR of C. rodentium LEE mRNAs in murine cecum tissue of animals infected with WT, ΔcutR, and complemented strains. (J) qRT-PCR of C. rodentium LEE mRNAs in murine colon tissue of animals infected with WT, ΔcutR, and complemented strains. (K) qRT-PCR of C. rodentium LEE mRNAs in murine cecum tissue of animals infected with WT, ΔfadR, and complemented strains. (L) qRT-PCR of C. rodentium LEE mRNAs in murine colon tissue of animals infected with WT, ΔfadR, and complemented strains. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. P.I., postinfection.