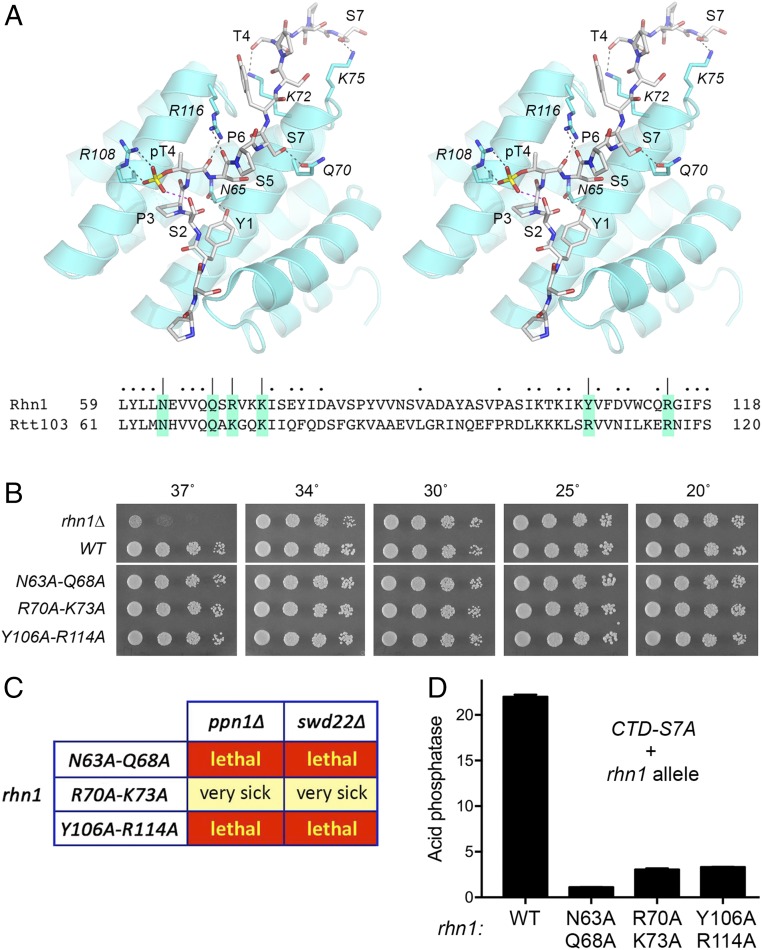
Fig. 7.
Effect of mutating the CTD-binding site of Rhn1. (A, Upper) Stereoview of the structure of the Rtt103 CTD-interaction domain in complex with a CTD peptide containing Thr4-PO4 (Protein Data Bank ID code 5LVF). The CTD peptide is depicted as a stick model with gray carbons; the CTD amino acids are labeled in plain font. Rtt103 side chains that contact the CTD are shown as stick models with cyan carbons and are labeled in italics. Hydrogen-bond interactions between Rtt103 and the CTD are indicated by black dashed lines; an intramolecular H-bond from Ser2-OH to the Thr4 phosphate is indicated by a magenta dashed line. (A, Lower) Alignment of the amino acid sequence of the CTD-interacting segment of Rtt103 to the equivalent segment of Rhn1. Amino acids targeted for Ala scanning in Rhn1 are shaded and denoted by |. Other positions of side-chain identity/similarity are indicated by dots above the Rhn1 sequence. (B) Serial dilutions of the indicated rhn1 strains were spot tested for growth on YES agar at the indicated temperatures. All rhn1 strains were spotted on the same agar plate in every case. The white space between the WT and N63A-Q68A spottings indicates that a single intervening row of cell spottings (of a strain not relevant to the experiment) was cropped out of the image. (C) Mutational synergies. Synthetically lethal pairs of alleles are highlighted in red boxes. The yellow boxes indicate a severe synthetic growth defect (very sick). (D) S. pombe strains bearing the rpb1-CTD-S7A allele in combination with Rhn1 mutants as specified were grown in liquid culture at 30 °C and were assayed for acid phosphatase activity. Each datum in the bar graph is the average of assays using cells from at least three independent cultures ± SEM.