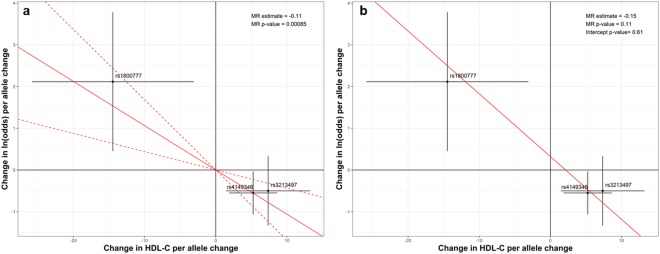
Figure 3.
Mendelian Randomization Results. (a) Inverse-variance weighting (IVW) analysis including the selected SNPs rs4149346 (ABCA1), rs1800777 (CETP), and rs3213497 (GALNT2). X-axis: changes in HDL-C (mg/mL) per allele change; Y-axis: changes in natural logarithm (ln) odds per allele change. Estimated effects on acute kidney injury (AKI) risk are plotted against estimated effects on serum HDL-C for 3 SNPs associated with HDL-C and AKI. IVW estimate: red solid lines; 95% CI: red dashed lines. SNPs associated with increased HDL-C levels decreased the risk of AKI by 11% (ln = −0.11, odds = 0.89) per 1 mg/dL increases in HDL-C, P = 0.00085). (b) Pleiotropy Analysis: no unbalanced pleiotropy in the IVW MR analysis was found (P = 0.61) as the intercept was not difference from 0. A negative (but less significant) effect of HDL-C on AKI was demonstrated: the risk of AKI decreased by 14% (ln = −0.15, odds = 0.86) per 1 mg/dL of increases in HDL-C (P = 0.11).