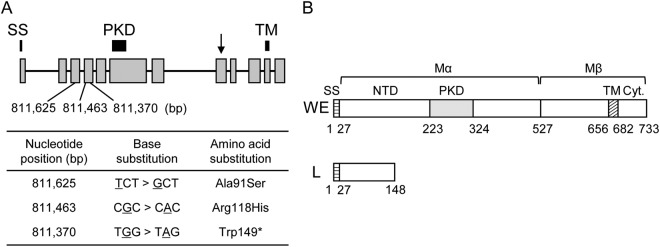
Figure 3.
Genomic positions of mutations in the PMEL gene and structures of wild-type and mutant-type PMEL proteins. (A) Schematic representation of the PMEL gene and nucleotide positions of mutations in LGE22. Grey boxes and black lines indicate exons and introns, respectively. Black bars indicate signal sequence (SS), polycystic kidney disease (PKD), and transmembrane (TM) domains. The arrow indicates the proteolytic cleavage site. Nucleotide positions (bp) of mutations in LGE22 in the quail genome assembly are indicated at the bottom of the diagram. The table indicates base substitutions and amino-acid substitutions due to these mutations. A nonsense mutation was found at the nucleotide position 811,370 in the fourth exon of the PMEL gene. Two missense mutations were found upstream of the nonsense mutation. (B) Schematic representation of deduced PMEL proteins of the WE and L strains. The PMEL of the WE strain contains SS, the amino-terminal domain (NTD), and PKD, TM, and cytoplasmic (Cyt.) domains. SS is removed cotranslationally, and Mα and Mβ fragments are generated by proteolytic cleavage in the Golgi apparatus or a post Golgi compartment31. The PMEL of the L strain contains SS and part of the NTD.