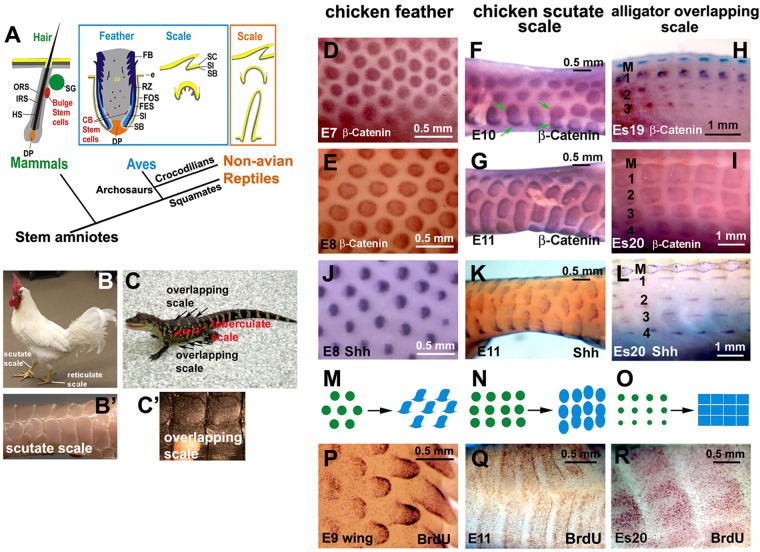
Figure 1.
Development of avian and reptilian scales. (A) Schematic drawing of the stem cell niche in mammalian hairs and avian feathers. (B) Adult chicken showing feathers and scales. (B’) Scutate scales. (C) Juvenile alligator showing different types of scales. (C’) Overlapping scale. D-I, β-catenin whole mount in situ hybridization. (D) E7 chicken dorsal feather tract (placode stage). (E) E8 chicken dorsal feather tract (short bud stage). (F) E10 chicken scutate scale (placode stage). Green arrows indicate the fusion of scutate scale placodes. (G) E11 chicken scutate scale (short bud stage). (H) Es19 alligator overlapping scale (placode stage). (I) Es20 alligator overlapping scale (short bud stage). (J–L) Shh whole mount in situ hybridization. J, E8 chicken dorsal feather tract. (K) E11 chicken scutate scale. (L) Es20 alligator overlapping scale. (M–O) Schematic drawing of skin appendage development. (M) Chicken feather, (N) chicken scutate scale, (O) alligator overlapping scale. (P–R) Whole mount BrdU staining. (P) Feather buds in an E9 chicken wing showed different feather developmental stages, from short buds to long buds. (Q) E11 chicken scutate scale. (R) Es20 alligator overlapping scale. Note the feathers have a broader localized growth zone than scales. CB, collar bulge; DP, dermal papilla; e, epidermis; FB; feather barb ridge; FES, feather sheath; FOS, feather follicle sheath; HS, hair shaft; IRS, inner root sheath; M, dorsal middle line of alligator embryo; ORS, outer root sheath; RZ, ramogenic zone; SG, sebaceous gland; SB, stratum basal; SC, stratum corneum; SI, stratum intermedium; 1, 2, 3, 4 indicate the row number with 1 closest to the middle of the dorsal region.