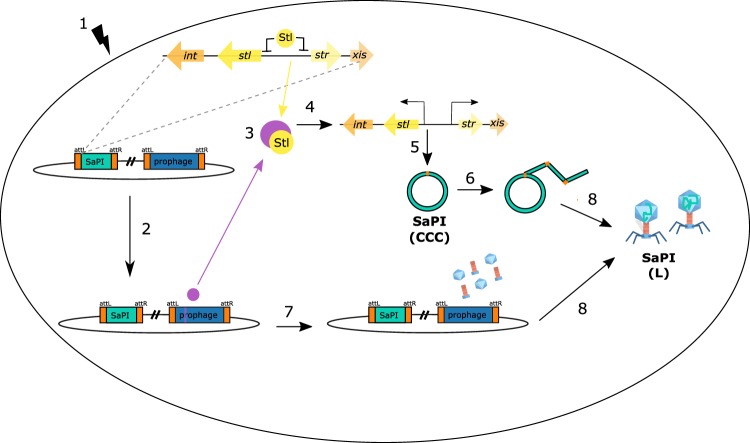
Figure 1.
SaPI cycle after prophage induction. (1) SOS response after mitomycin C addition. (2) The prophage is induced and start the gene transcription, while the SaPI resides passively in the genome under the control of the global repressor Stl. (3) The interaction between the Stl and a specific phage derepressor protein induces the SaPI cycle. (4) The SaPI gene transcription starts. (5) SaPI is excised from the chromosome in covalently closed circular (CCC) state and (6) starts the replication. (7) The phage synthetises the procapsids and tails. (8) SaPI L indicates linear monomers released from the phage heads if the prophage is able to mobilise the SaPI.