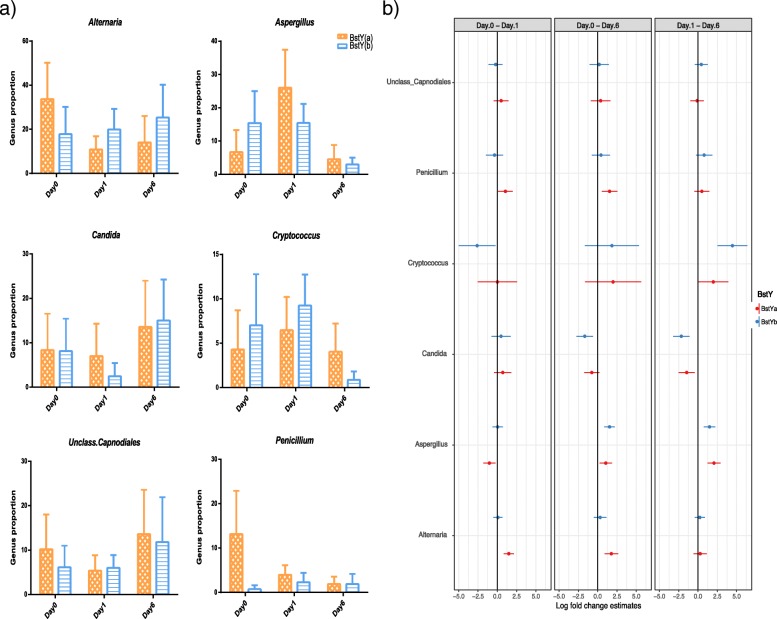
Fig. 5.
Dynamics of fungal communities of intramammary microbiota during the first week of lactation. a Bar graphs show the proportion of predominant fungal genera of intramammary secretions during the first week of lactation. Color codes were used to relate the average proportion of genera to BoLA variants, x-axis relates the proportion of bacterial genera to days in milk, and error bars denote 95% confidence intervals. b Associations of bacterial genera with BoLA variants and DIM were analyzed with generalized linear mixed effect model (package glmmTMB). The total count of OTUs assigned to each genus were offset to the library size (total count of OTUs detected in each sample) and then used as the response variable in a negative binomial model where BoLA variants, DIM, and their interaction were included as fixed effects, whereas the effect of individual cows were included as the random effect. Estimated group means, confidence intervals (CI), and pairwise comparisons for effects of BstY variants and DIM were derived using the package emmeans. Multiple hypotheses were adjusted by Benjamini and Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR). Genera for which the high and low values of CI do not cross the zero line show significant log fold change between DIM contrasts. Summary statistics are available in Additional file 2: Table S4