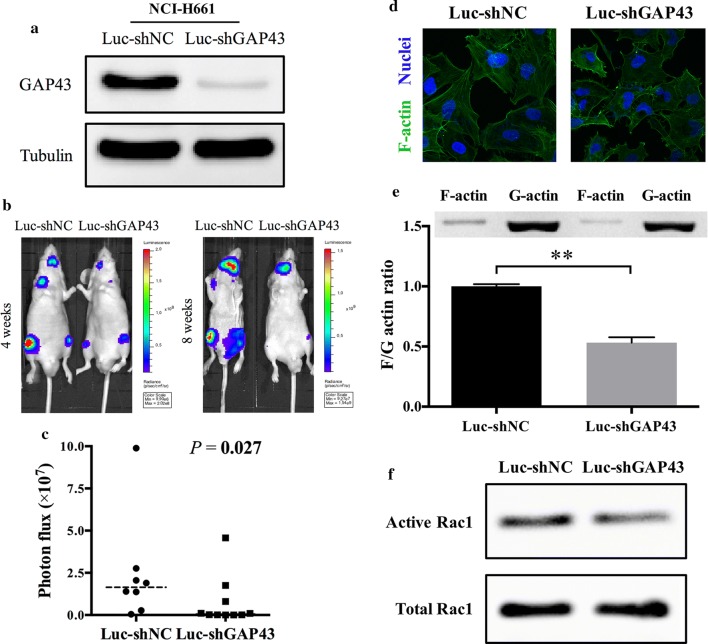
Fig. 4.
GAP43 depletion decreased metastasis in vivo and triggered F-actin depolymerization. a Validation of stable GAP43 knockdown in NCI-H661 cells by western blotting. b Representative images of bioluminescence 4 and 8 weeks after left ventricular injection of NCI-H661-Luc-shNC and NCI-H661-Luc-shGAP43 cells. c Quantification of bioluminescence in the 8th week. Each group had 10 mice, while 2 mice in the NCI-H661-Luc-shNC group died soon after the injection of left ventricle. The P value was determined using a Mann–Whitney U test. d Representative images of F-actin immunofluorescence in NCI-H661-Luc-shNC and NCI-H661-Luc-shGAP43 cells. e Expression levels of F-actin and G-actin in NCI-H661-Luc-shNC and NCI-H661-Luc-shGAP43 cells examined by western blotting and a histogram of the F-actin/G-actin ratio. F-actin was depolymerized and decreased after GAP43 knockdown. The P value was estimated with Student’s t-test. f Detection of active and total Rac1 in NCI-H661-Luc-shNC and NCI-H661-Luc-shGAP43 cells by western blotting. Active Rac1 decreased and total Rac1 remained unchanged after GAP43 depletion. **P < 0.01