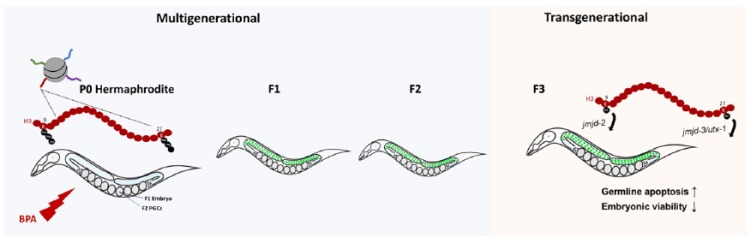
Figure 1.
BPA exposures in C. elegans reduces the levels of the repressive histone marks H3K9me3 and H3K27me3, regulated by the demethylases jmjd-2 and jmjd-3/utx-1, respectively. This disruption causes a de-silencing effect and reproductive dysfunction observed from the P0 generation until the F4. The F3 generation represents the first generation where there was no direct contact with the environmental toxicant (BPA).