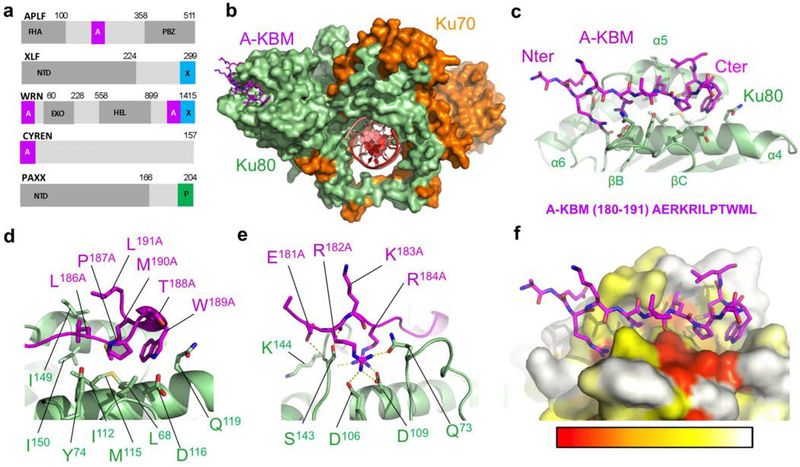
Figure 1. Crystal structure of the APLF KBM (A-KBM) bound to the Ku80 vWA domain.
(a) Positions of the A-KBM (magenta) and X-KBM (blue) motifs in APLF, XLF, WRN and CYREN. The C-terminal domain of PAXX contains a P-KBM that interacts with Ku70 subunit. NTD: N-terminal domain. (b) Overall view of the quaternary complex Ku70/Ku80/hDNA/(APLF peptide). The A-KBM (magenta) binds at the periphery of the Ku80 (light green) vWA domain. The Ku70 subunit and hDNA are represented respectively in orange and red. The hairpin part of the DNA has been removed for clarity. (c) The N-terminal part of the A-KBM motif has an extended conformation whereas the C-terminal residues form a turn. (d-e) Zoom of the interactions made by (d) the hydrophobic patch and (e) the basic patch of the A-KBM. (f) The A-KBM binding site is delineated by conserved residues of Ku80 vWA domain. The binding site is represented in surface mode with amino acids colored according to their conservation rate: red (highly conserved) to white (not conserved)). The conservation rate was measured using sequences of metazoan Ku80. The orientation is the same as in (c).