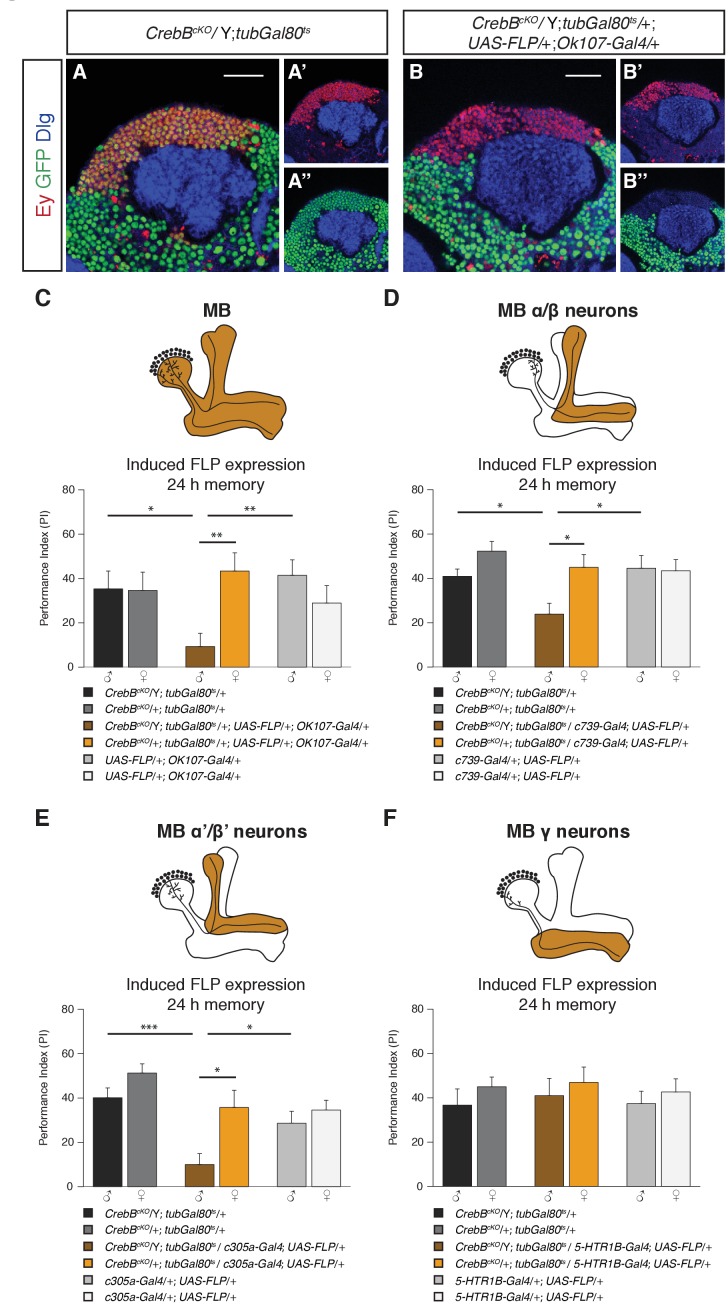
Figure 3. CrebB is required in MB α/β and MB α’/β’ neurons for LTM formation.
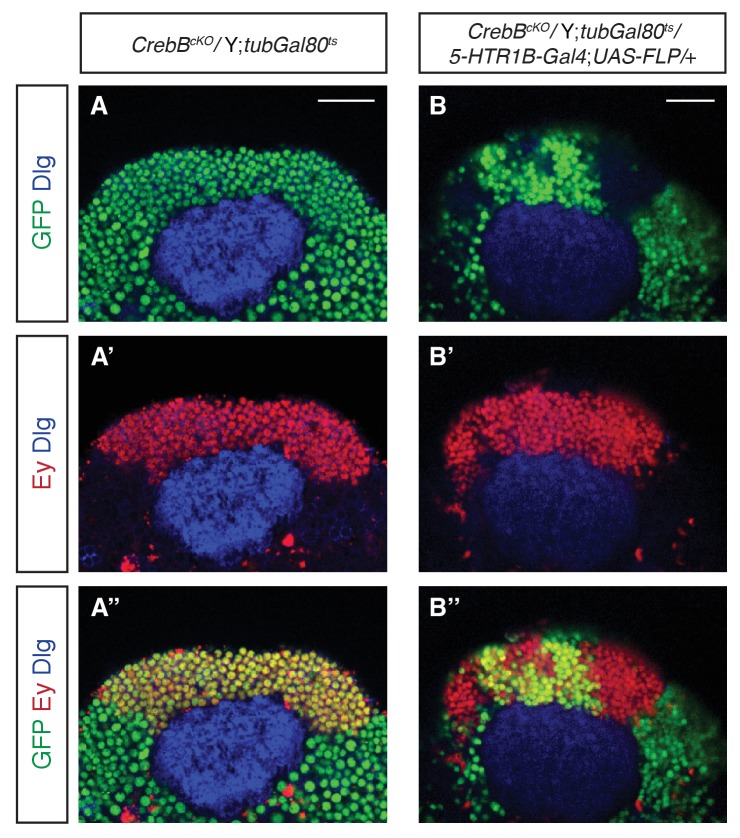
(A, B) Brains were stained using anti-GFP (green), anti-Discs large (Dlg, blue) and anti-Eyeless (Ey, red) antibodies, which labels Kenyon cells. (A–A’’) CrebB::GFP is expressed in Kenyon cells of CrebBcKO; tubGal80ts male flies. (B–B’’) After induction of mushroom body-specific CrebB::GFP knockout, Ey-expressing Kenyon cells lost GFP expression. Scale bars: 25 μm. (C–F) Different MB-Gal4 driver lines were used to induce deletion of CrebB in Kenyon cells and to test for the requirement of CrebB for 24 h memory. (C) Induction of CrebB knockout in the entire MB using OK107-Gal4 severely impaired LTM. N ≥ 10. (D, E) The 24 h memory scores were significantly reduced by the knockout of CrebB in MB α/β neurons with c739-Gal4 (N ≥ 9) and in MB α’/β’ neurons with c305a-Gal4 (N ≥ 8). (F) CrebB knockout in MB γ neurons with 5-HTR1B-Gal4 did not impair LTM formation. No significant difference was observed between the tested groups. N ≥ 8. Bar graphs represent the mean and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Asterisks denote significant differences between groups; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (Welch two sample t-test).