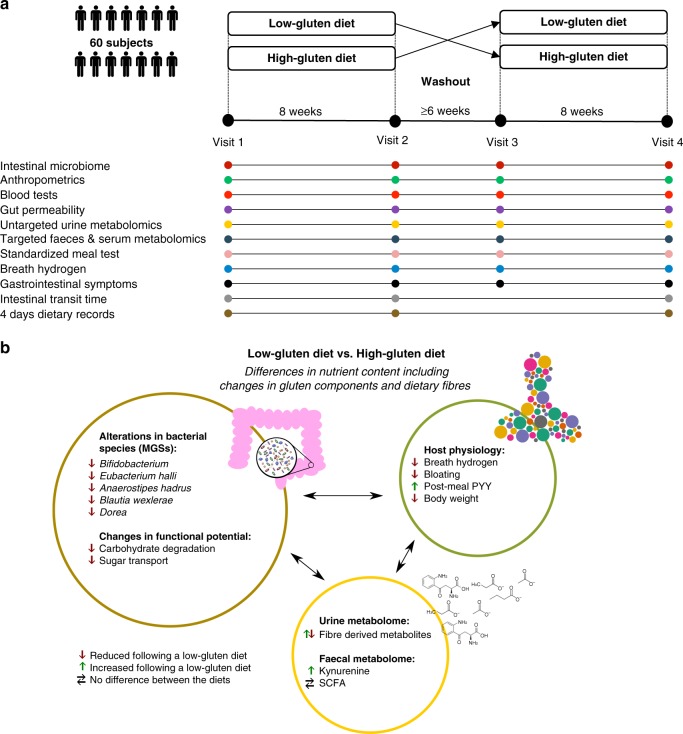
Fig. 1.
Experimental design, data overview and summary of the cross-over trial. a The study was a randomised, controlled, cross-over trial with two 8-week dietary intervention periods separated by a washout period of at least six weeks, comparing the effects of a low-gluten diet and a high-gluten diet on the gut microbiome (predefined primary outcome), untargeted urine metabolome and measures of host physiology12. Time points for data collections are indicated by circles in the lower part panel (a). b Effects of a low-gluten diet compared with a high-gluten diet on the intestinal microbiome, urine/faecal metabolome and markers of host physiology in apparently healthy adults. Measured variables that were found to be reduced (red arrow), increased (green arrow) or unchanged (black horizontal arrows) following the low-gluten diet intervention compared with the high-gluten diet intervention are listed. MGS metagenomics species, PYY peptide YY, SCFA short-chain fatty acids. The person icon and molecular structure images for the acetate anion, butyrate ion, propionate ion and kynurenine were obtained from Wikimedia Commons, released under public domain