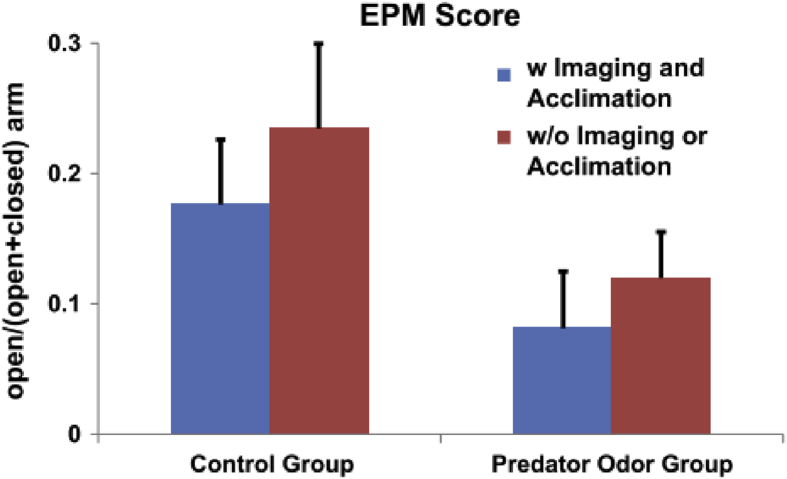
Fig. 6.
Relative behavioral effect induced by a single trauma exposure and acclimation. In all 32 rats, 16 rats underwent the acclimation and imaging procedures (among them 8 rats were exposed to predator odor and the other 8 rats were exposed to air). The other 16 rats were not acclimated or imaged (8 were exposed to predator odor and the other 8 were exposed to air). The EPM score (open/(open + closed) arm) was separately assessed for all four subgroups. Two-way ANOVA with the factors of acclimation and trauma exposure was applied to the four groups. Our results (p_acclimation = 0.34, p_trauma exposure <0.05 and p_interaction = 0.85) confirmed a much smaller effect of acclimation than trauma exposure. They also showed a minimal interaction between the trauma-induced stress and acclimation/imaging-related stress. Adapted from (Liang et al., 2014).